IBM and AMD partner on quantum-centric supercomputing, merging quantum with HPC and AI to enable hybrid workflows and accelerate discovery.
IBM and AMD are taking center stage in shaping the future of technology by embarking on a groundbreaking collaboration. Together, they aim to pioneer quantum-centric supercomputing, an advanced architecture that seamlessly integrates quantum processors with high-performance computing (HPC) and AI infrastructure. This joint effort is designed to harness the unique strengths of AI accelerators, HPC, and quantum systems, enabling organizations to tackle some of the world’s most formidable challenges. By combining their expertise, IBM and AMD are setting the stage for transformative breakthroughs in fields ranging from medicine to logistics.
At the heart of this initiative is a recognition that quantum computing offers a fundamentally different approach to representing and processing information. Classical systems rely on bits that exist as either 0 or 1. Quantum computers, on the other hand, employ qubits that harness the principles of quantum mechanics, enabling them to occupy multiple states simultaneously. This enables quantum systems to explore vast solution spaces that classical machines cannot easily access, particularly in fields such as drug and material discovery, optimization, and large-scale logistics.
Combining the Strengths of AMD and IBM
IBM brings significant expertise to this domain, having built the world’s most performant quantum computers and advanced software ecosystems, including the open-source Qiskit framework. AMD complements this strength with proven leadership in high-performance computing and AI accelerators, backed by a track record of powering the world’s fastest supercomputers. Together, the companies envision building scalable, open platforms that redefine how hybrid computing workloads are designed and executed.
IBM Chairman and CEO Arvind Krishna describes quantum computing as a turning point in how information will be represented and simulated. He emphasizes that the collaboration with AMD is designed to establish a hybrid computing model where quantum and classical systems complement each other, thereby exceeding the limitations of traditional architectures.
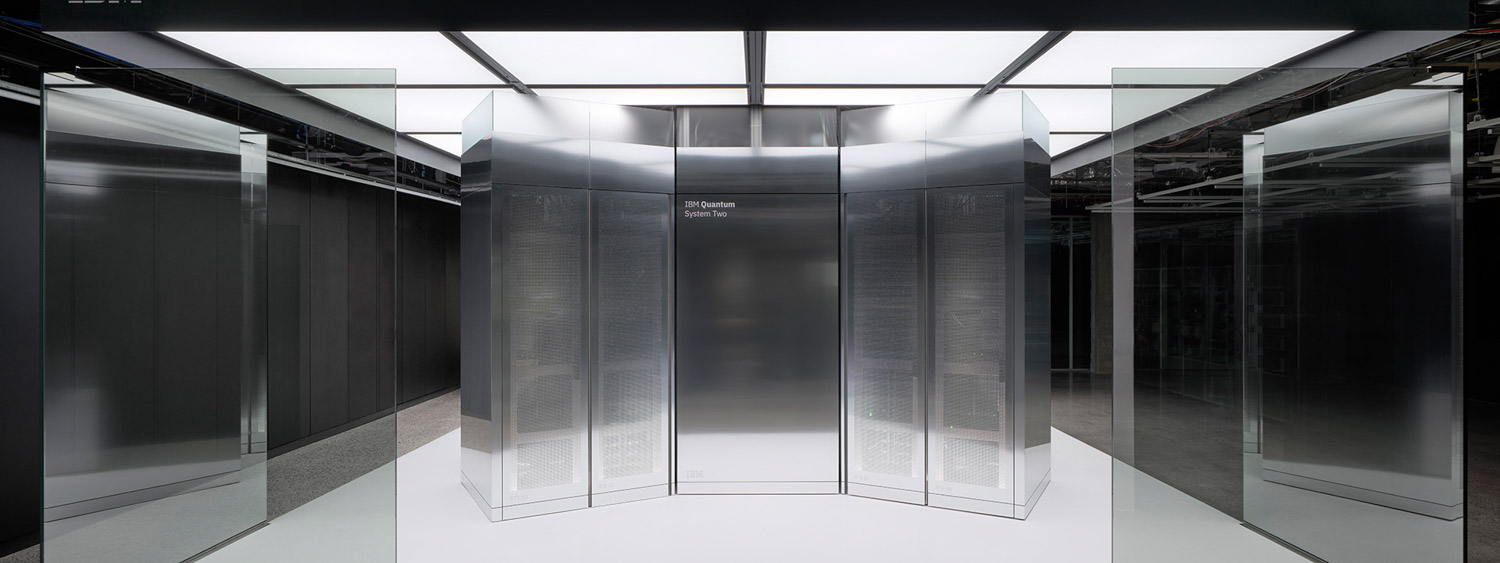 For AMD, collaboration is equally strategic. Dr. Lisa Su, Chair and CEO, emphasizes that high-performance computing will remain central to tackling global challenges such as healthcare, climate modeling, and energy innovation. She highlights the partnership with IBM as an opportunity to accelerate discovery by uniting HPC and quantum technologies into a more capable, hybrid platform.
For AMD, collaboration is equally strategic. Dr. Lisa Su, Chair and CEO, emphasizes that high-performance computing will remain central to tackling global challenges such as healthcare, climate modeling, and energy innovation. She highlights the partnership with IBM as an opportunity to accelerate discovery by uniting HPC and quantum technologies into a more capable, hybrid platform.

Toward a Quantum-Centric Architecture
In the proposed model, quantum computers will not operate in isolation. Instead, they will work in tandem with powerful HPC and AI infrastructures—leveraging CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs to form cohesive computational workflows. Tasks will be allocated to the paradigm best suited to handle them. For example, quantum systems might simulate molecular interactions at the atomic scale, while GPU-powered supercomputers analyze accompanying datasets. This orchestration promises not only unprecedented speed but also a more scalable and efficient approach to solving real-world challenges.
An area of strong collaboration is in fault-tolerant quantum computing, a milestone many experts believe will be achieved by the end of this decade. AMD’s CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs could play a crucial role in providing the real-time error correction needed to stabilize large quantum workloads. Both companies are also exploring how open-source communities can accelerate the adoption of quantum-centric supercomputing. Qiskit, for instance, may serve as a foundation for new hybrid algorithms that exploit the advantages of both paradigms.
Demonstrations and Industry Momentum
Later this year, IBM and AMD plan to showcase an integrated workflow that demonstrates how quantum processors can interoperate with AMD technologies. This demonstration will highlight the value of hybrid execution models and serve as a reference for further development.
IBM’s existing collaborations reinforce its vision for quantum-classical integration. In Japan, IBM partnered with RIKEN to connect the modular IBM Quantum System Two with Fugaku, one of the fastest supercomputers in the world. Other collaborations, including projects with the Cleveland Clinic, the Basque Government, and Lockheed Martin, have shown how quantum-classical systems can outperform classical-only approaches for certain complex problem domains.
AMD, meanwhile, continues to define the HPC frontier. Its EPYC CPUs and Instinct GPUs power Frontier at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the world’s first exascale supercomputer, and El Capitan at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory—the two top-ranked systems on the latest TOP500 list. Beyond HPC, AMD’s CPUs, GPUs, and open software ecosystems are accelerating the adoption of generative AI across industries and cloud platforms worldwide.
Looking Ahead
The collaboration between IBM and AMD reflects a pivotal shift in the computing landscape. By converging quantum, HPC, and AI ecosystems, the companies are laying the groundwork for systems that can solve problems well beyond the limits of classical computation. Though still in the early phases, these hybrid architectures could shape the next decade of innovation, helping industries unlock discoveries that were once considered unreachable.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed
