Big Data comes up frequently in data management. Harnessing Big Data can lead businesses to all sorts of insights that could make them more efficient and more profitable. The only problem is that using Big Data can be quite the arduous undertaking when it comes to resource management and system administration. Google plans to tackle Big Data the “cloud way” with Google Cloud Platform and updates to its BigQuery and the introduction of Cloud Dataflow.
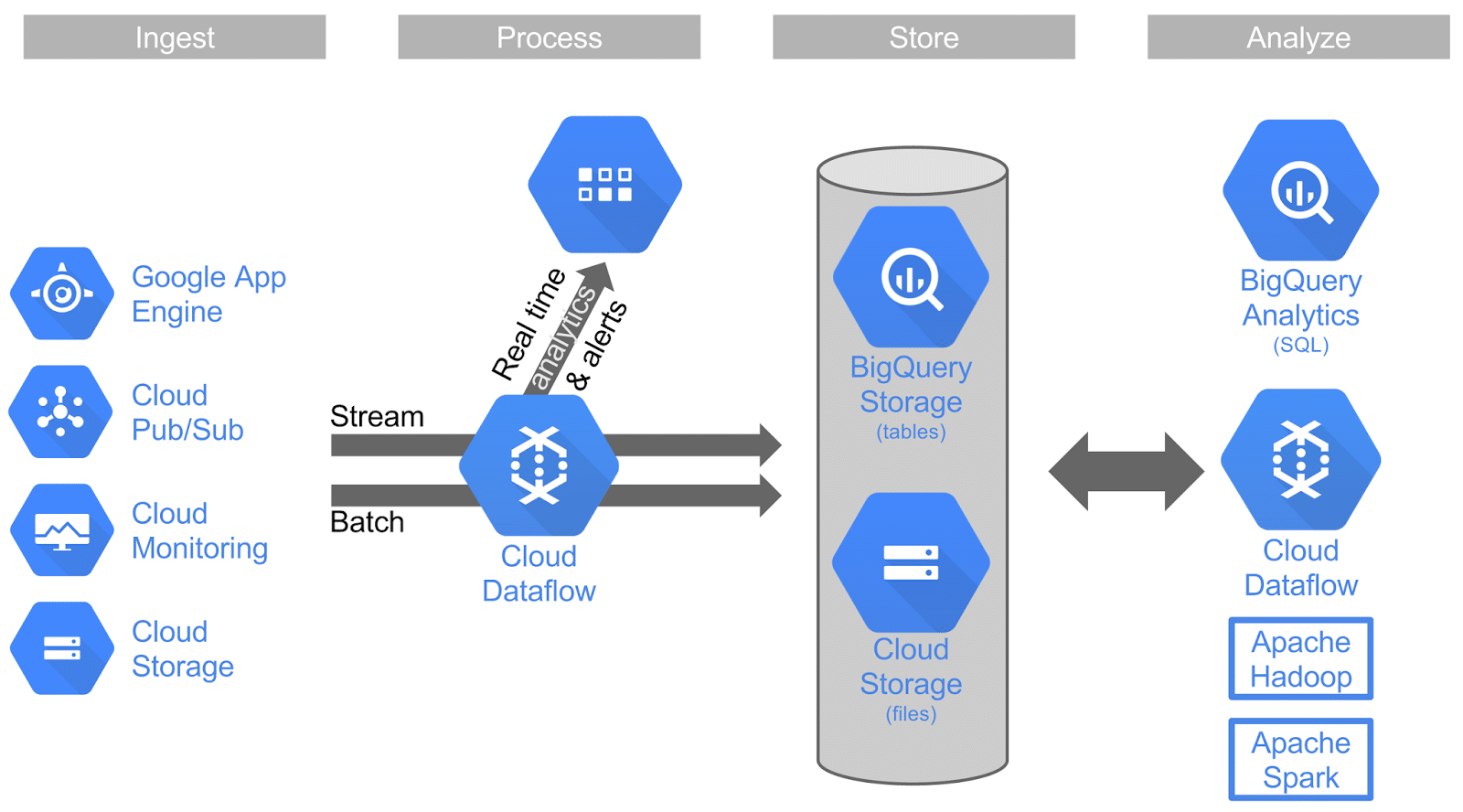
Google Cloud Platform is offering a set of powerful, scalable, and easy-to-use Big Data services so customers can embrace Big Data, the cloud way. The first of which is Google Cloud Dataflow, which provides reliable, event-time-based stream processing, available by default. The second is through updates to Google’s BigQuery, the quintessential cloud-native, API-driven service for SQL analytics. These updates include security and performance features including row-level permissions, now with a default ingestion limit to 100,000 rows/second/table.
Google’s cloud way of handling Big Data is aimed at gaining faster and better insights into Big Data without worrying about the underlying infrastructures. It includes:
- NoOps: “NoOps” means the platform handles such tasks and optimizations for users, freeing them up to focus on understanding and exploiting the value in their data.
- Cost effectiveness: the platform auto-scales and optimizes user’s infrastructure consumption, and eliminates unused resources like idle clusters. Users manage costs by dialing up or down the number of queries and the latency of their processing based on cost/benefit analysis.
- Safe and easy collaboration: Users can share datasets from files in Google Cloud Storage or tables in Google BigQuery with collaborators inside or outside of their organization without the need to make copies or grant database access.
Along with BigQuery and Cloud Dataflow, Google rounds out its Big Data, the cloud way with Google Cloud Pub/Sub. Pub/Sub allows users to handle data processing with low-latency in real-time.
Availability
Google BigQuery is available now with the options of storing data in Google Cloud Platforms in European zones and Google Cloud Dataflow is available in beta.




 Amazon
Amazon