Following a brief reveal during COMPUTEX 2025, AMD’s Radeon RX 9060 XT has now officially launched, targeting gamers who want strong 1080p and 1440p performance at a more accessible price point. We previously reviewed the RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT, which delivered solid results in the midrange segment. Now, the RX 9060 XT lowers the entry point further, with pricing set at $379 for the 16GB model and $299 for the 8GB version. AMD’s price point here puts it under NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 5060 Ti, positioning this card as a better value for budget-conscious buyers.
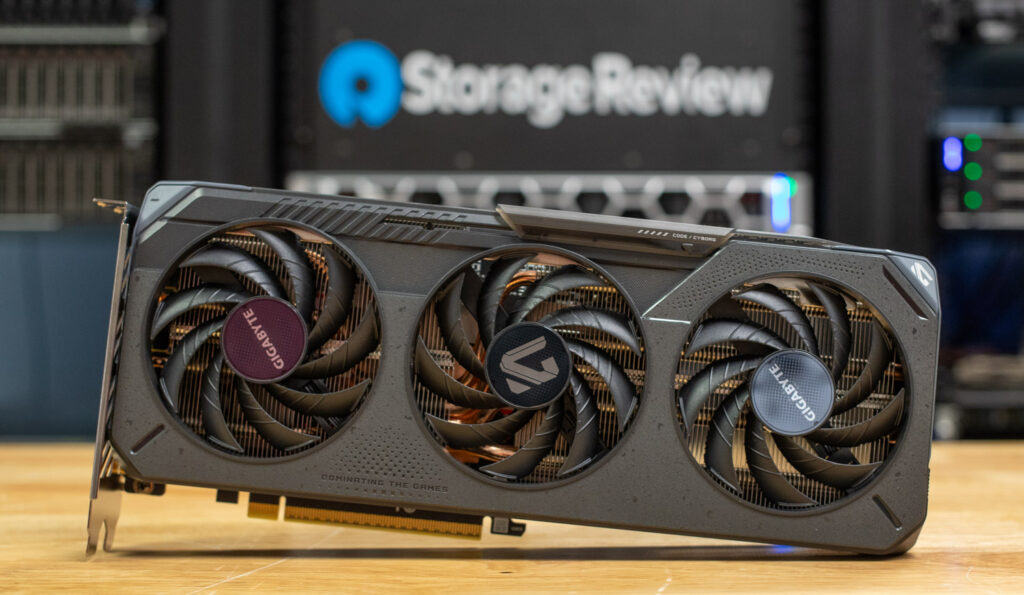
AMD provided us with the RX 9060 XT for testing, and we specifically examined the Gigabyte Radeon RX 9060 XT GAMING OC 16G variant. This factory-overclocked model features a triple-fan cooler, a metal backplate for added rigidity, and a design that emphasizes both thermal efficiency and quieter operation. With the full feature set of AMD’s RDNA 4 architecture now detailed, we can evaluate how this card performs in real-world gaming, ray tracing, and AI-enhanced workloads and see how it stacks up against its higher-tier counterparts.

AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT Architecture
The RX 9060 XT is built on AMD’s RDNA 4 architecture, a substantial advancement over previous generations that focuses on delivering improved efficiency, enhanced performance per watt, and expanded capabilities across compute, ray tracing, AI, and media. At the core of this architecture are redesigned compute units that benefit from improved memory subsystems and more optimized data pathways throughout the GPU. Compared to RDNA 3, RDNA 4 compute units offer up to 40 percent more performance per CU, enabling the RX 9060 XT to reach boost clocks over 3GHz while maintaining competitive power consumption levels. These gains are crucial for bringing high-end features to the mainstream tier without increasing platform requirements.
Ray tracing performance also received a significant overhaul. The RX 9060 XT features AMD’s third-generation RT accelerators, which include a second ray intersection engine that doubles throughput for both ray-box and ray-triangle operations. New dedicated ray transformation hardware further enhances performance, especially during the deep traversal of bounding volume hierarchies. In addition, the introduction of Oriented Bounding Boxes improves how geometry is processed by reducing BVH complexity and memory overhead. These improvements make real-time ray tracing more viable in a broader range of games, even at this price point.
AI acceleration represents one of the most significant leaps in RDNA 4. The RX 9060 XT features AMD’s second-generation AI accelerators, which deliver significantly faster throughput than previous designs by expanding math pipelines and supporting modern data types, such as FP8. These units support inference techniques such as structured sparsity, which allow more efficient execution of AI workloads across gaming, content creation, and upscaling applications. In real-world terms, these improvements enable FidelityFX Super Resolution 4 (FSR4) to deliver image quality that surpasses native resolution in supported titles, while also enhancing performance through advanced frame generation. FSR4 builds on FSR 3.1, featuring a machine learning core optimized for RDNA 4 hardware. Additionally, AMD has made it backward-compatible with existing game engines, facilitating easier adoption.
The RX 9060 XT also benefits from an updated media and display engine. AMD’s Radiance Display Engine supports DisplayPort 2.1a, unlocking higher refresh rates and future-proofing the card for next-generation monitors. AV1 encode and decode support has also been improved, allowing for smoother video playback, lower bitrate streaming, and cleaner recording. This upgrade positions the RX 9060 XT as a capable tool not only for gaming but also for content creation and live streaming workflows.
| Specifications Overview | AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT |
|---|---|
| Family | Radeon RX |
| Series | Radeon RX 9000 Series |
| Board Type | Desktop |
| OS Support | Windows 10/11 (64-bit), Linux x86 64-bit |
| Additional Power Connector | 1x 8-Pin |
| Compute Units | 32 |
| Stream Processors | 2048 |
| Ray Accelerators | 32 |
| AI Accelerators | 64 |
| Boost Frequency | Up to 3130 MHz |
| Game Frequency | 2530 MHz |
| ROPs | 64 |
| Texture Units | 128 |
| Transistor Count | 29.7 Billion |
| Typical Board Power | 160W |
| Minimum PSU Recommendation | 450W |
| Memory Size | 16 GB GDDR6 or 8 GB GDDR6 |
| Memory Interface | 128-bit |
| Memory Bandwidth | Up to 320 GB/s |
| Memory Speed | Up to 20 Gbps |
| Infinity Cache | 32 MB |
| Peak FP16 Compute | 51.3 TFLOPs |
| Peak FP32 Compute | 25.6 TFLOPs |
| Peak INT4 Performance | 821 TOPs |
| Peak INT8 Performance | 410 TOPs |
| Peak Pixel Fill-Rate | Up to 200.3 GP/s |
| DisplayPort™ | 2.1a |
| HDMI™ | 2.1b |
| AV1 Encode/Decode | Yes |
| H265 Encode/Decode | Yes |
| Price USD | $379 16GB | $299 8GB |
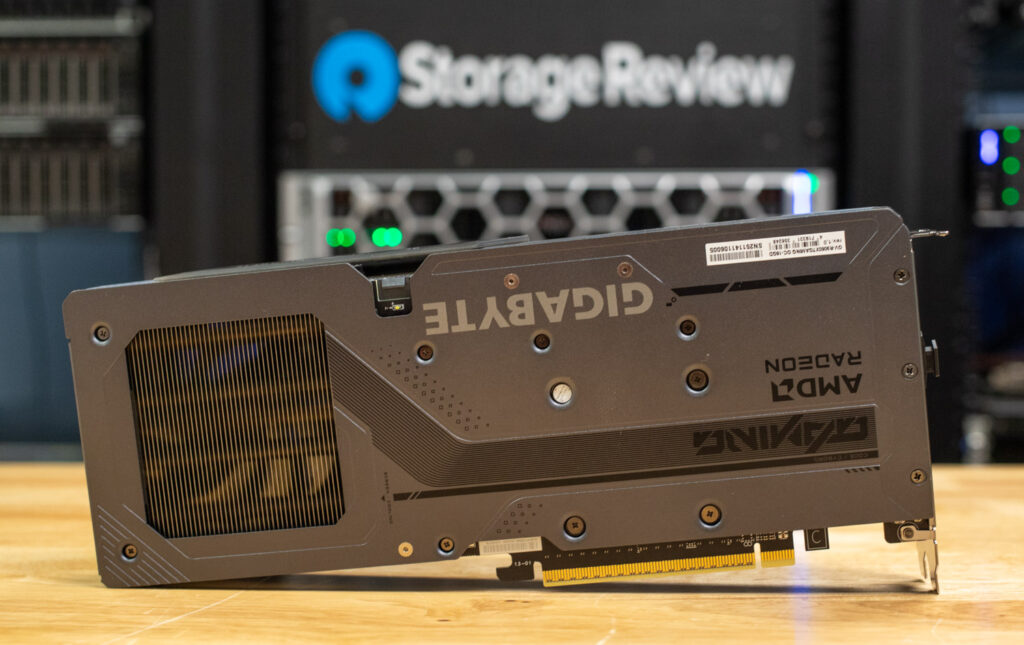
Build and Design AMD Gigabyte Radeon RX 9060 XT GAMING OC 16G
The AMD Gigabyte Radeon RX 9060 XT is a dual-slot graphics card featuring Gigabyte’s WINDFORCE cooling system, which uses three uniquely designed HAWK FANS. These fans incorporate Gigabyte’s blade design to enhance airflow and maintain efficient cooling while keeping noise levels low during operation. The card is equipped with 16GB of GDDR6 memory on a 128-bit interface, offering solid performance for gaming and creative tasks. Fan noise on this GPU was nearly non-existent during tests, and under idle loads, the fans completely stopped.
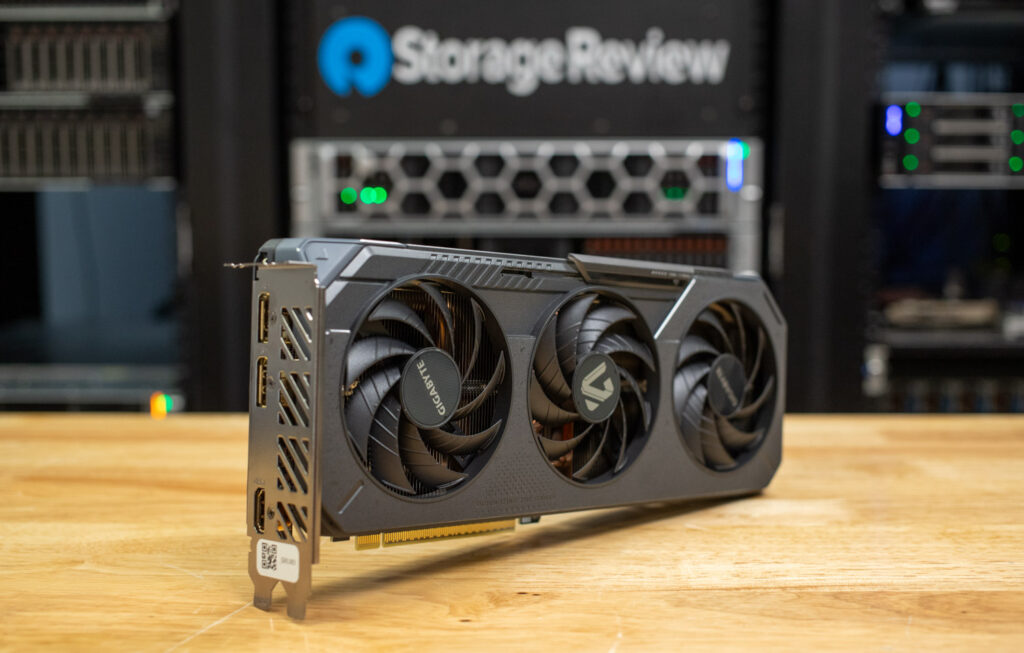

The underside of the card doesn’t reveal much at first glance, but it does showcase the attention Gigabyte has put into the cooling solution. A large copper base plate and composite copper heat pipes are used to draw heat away from key components efficiently. To ensure optimal thermal transfer, Gigabyte applies a server-grade thermal conductive gel between the GPU and the cooling interface, enhancing overall heat dissipation.
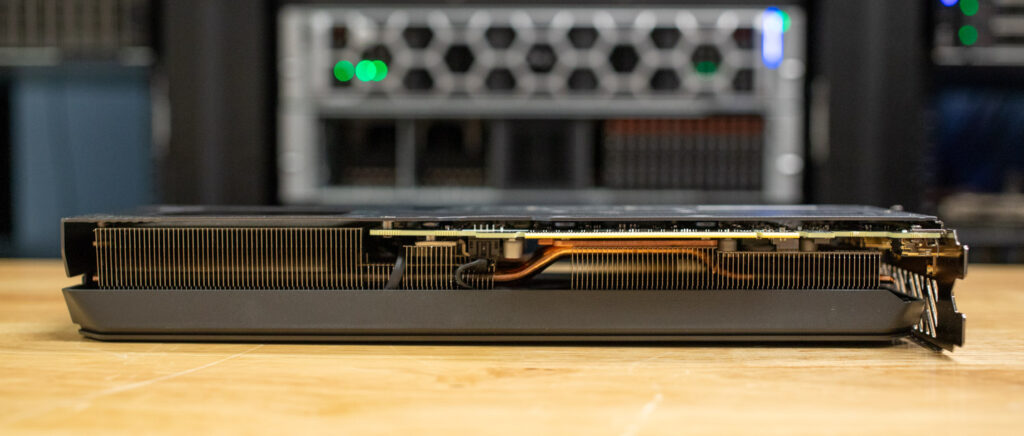

On the top side of the card, there’s a single 8-pin power connector that supplies the necessary power for its 160W TDP. For added aesthetics, Gigabyte includes RGB lighting on the Gigabyte logo, while the Radeon branding remains non-illuminated.

On the PCIe end of the card, there’s a sturdy metal dual-slot bracket that houses the display outputs. It includes two DisplayPort 2.1a ports and one HDMI 2.1b port, supporting resolutions up to 7680 × 4320. This setup allows for high-resolution displays or multi-monitor configurations.
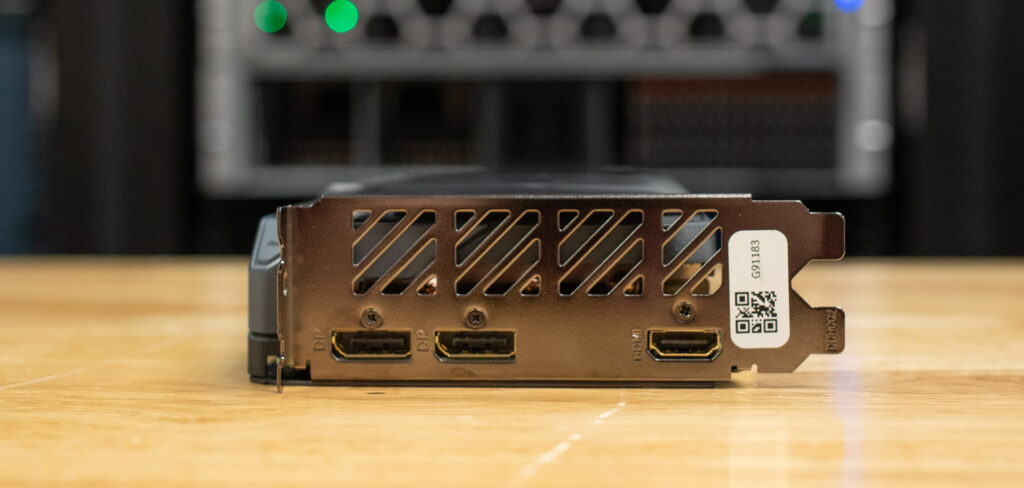

On the back side of the card, Gigabyte includes a black aluminum backplate that adds structural rigidity while also contributing to cooling. A cutout near the end of the card allows for improved airflow through the heatsink. The backplate also features subtle Gigabyte and Radeon branding for a clean, finished look.

Benchmarking: Gigabyte Radeon RX 9060 XT GAMING OC 16G
To test the new Radeon RX 9060 XT card from Gigabyte, we utilized our high-performance AMD Threadripper platform, which features a 64-core CPU and a custom water cooling loop. This setup ensures the GPU operates at full capacity without CPU bottlenecks. For comparison, the Gigabyte Radeon RX 9060 XT was tested on this configuration, alongside the AMD ASUS Prime Radeon RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT, the PNY NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti, the NVIDIA Founders Edition RTX 4070, and lastly, the ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti.
Below is the complete system configuration.
StorageReview AMD Threadripper Test Platform
- Motherboard: ASUS Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI
- CPU: AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X 64-Core
- RAM: 128GB DDR5 4800MT/s
- Storage: 2TB Samsung 980 Pro
- OS: Windows 11 Pro for Workstations
- Driver: AMD Adrenalin 25.3.1
UL Procyon: AI Text Generation
The Procyon AI Text Generation Benchmark simplifies AI LLM performance testing by offering a compact and consistent evaluation method. It allows for repeated testing across multiple LLM models while minimizing the complexity of large model sizes and variable factors. Developed with AI hardware leaders, it optimizes the use of local AI accelerators for more reliable and efficient performance assessments. The results measured below were tested using TensorRT on the NVIDIA models and ONNX for the AMD models.
In the Procyon AI Text Generation Benchmark, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT consistently placed at the bottom across all tested LLMs. It scored 1,281 in Phi, 1,274 in Mistral, 1,150 in Llama3, and 1,252 in Llama2. These results fall well below the RX 9070 XT’s scores, which ranged from 2,070 to 2,298, and even further behind NVIDIA’s midrange and upper-tier cards, where the RTX 5070 Ti peaked at 4,412 in Mistral and 4,284 in Llama2. The RX 9060 XT also showed the slowest tokens per second, with just 94.453 tokens/s in Phi, 65.115 tokens/s in Mistral, 53.167 tokens/s in Llama3, and 34.654 tokens/s in Llama2. Its time-to-first-token values were also the longest across the board. Overall, the RX 9060 XT lags behind in text generation tasks, delivering entry-level inference performance that is significantly lower than that of both higher-tier AMD models and all tested NVIDIA GPUs.
| UL Procyon: AI Text Generation | AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 FE | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 Ti |
| Phi Overall Score | 1,281 | 1,933 | 2,080 | 2,870 | 3,453 | 4,179 |
| Phi Output Time To First Token | 1.473 s | 0.954 s | 0.855 s | 0.375 s | 0.323 s | 0.290 s |
| Phi Output Tokens Per Second | 94.453 tokens/s | 139.187 tokens/s | 144.471 tokens/s | 120.773 tokens/s | 150.435 tokens/s | 192.487 tokens/s |
| Phi Overall Duration | 39.365 s | 26.989 s | 25.587 s | 25.216 s | 20.302 s | 15.771 s |
| Mistral Overall Score | 1,274 | 2,040 | 2,231 | 2,807 | 3,562 | 4,412 |
| Mistral Output Time To First Token | 1.827 s | 1.109 s | 0.946 s | 0.526 s | 0.433 s | 0.374 s |
| Mistral Output Tokens Per Second | 65.115 tokens/s | 101.300 tokens/s | 103.348 tokens/s | 91.057 tokens/s | 120.507 tokens/s | 160.167 tokens/s |
| Mistral Overall Duration | 54.516 s | 34.960 s | 33.350 s | 33.377 s | 25.496 s | 19.480 s |
| Llama3 Overall Score | 1,150 | 1,904 | 2,070 | 2,599 | 3,125 | 4,187 |
| Llama3 Output Time To First Token | 1.632 s | 0.981 s | 0.845 s | 0.449 s | 0.379 s | 0.306 s |
| Llama3 Output Tokens Per Second | 53.167 tokens/s | 87.594 tokens/s | 89.102 tokens/s | 74.709 tokens/s | 100.388 tokens/s | 131.583 tokens/s |
| Llama3 Overall Duration | 62.563 s | 38.273 s | 36.742 s | 39.489 s | 29.720 s | 22.786 s |
| Llama2 Overall Score | 1,252 | 2,047 | 2,298 | 2,576 | 3,125 | 4,284 |
| Llama2 Output Time To First Token | 2.992 s | 1.926 s | 1.565 s | 0.844 s | 0.785 s | 0.560 s |
| Llama2 Output Tokens Per Second | 34.654 tokens/s | 59.673 tokens/s | 61.127 tokens/s | 41.386 tokens/s | 56.647 tokens/s | 75.905 tokens/s |
| Llama2 Overall Duration | 99.027 s | 59.100 s | 55.520 s | 71.302 s | 53.234 s | 39.545 s |
UL Procyon: AI Image Generation
The Procyon AI Image Generation Benchmark consistently and accurately measures AI inference performance across various hardware, from low-power NPUs to high-end GPUs. It includes three tests: Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) for high-end GPUs, Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) for moderately powerful GPUs, and Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) for low-power devices. The benchmark uses the optimal inference engine for each system, ensuring fair and comparable results.
In the Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) test, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT scored 1,436, making it the lowest performer among the GPUs tested. It was outpaced by the RTX 5060 Ti at 2,110, the RX 9070 at 2,280, and the RX 9070 XT at 2,598. The RTX 5070 FE scored 2,937, while the ASUS PRIME RTX 5070 Ti led with 3,755. A similar trend appeared in the Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) test, where the RX 9060 XT scored just 1,124. In contrast, the RTX 5060 Ti posted 1,940, and the highest result again came from the RTX 5070 Ti at 3,352. The RX 9060 XT and other AMD models in this test do not support INT8 inference, resulting in no scores in that category, whereas NVIDIA cards performed well in this test. Overall, the RX 9060 XT trails the rest of the lineup in AI inference workloads, performing below both AMD’s higher-tier models and all tested NVIDIA GPUs.
| UL Procyon: AI Image Generation (overall score: higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 FE | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 Ti |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) — Overall Score | 1,436 | 2,110 | 2,280 | 2,598 | 2,937 | 3,755 |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) — Overall Time | 69.633 s | 47.590 s | 43.858 s | 38.481 s | 34.038 s | 26.625 s |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) — Image Generation Speed | 4.352 s/image | 2.974 s/image | 2.741 s/image | 2.405 s/image | 2.127 s/image | 1.664 s/image |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) — Overall Score | N/A | 27,705 | N/A | N/A | 36,320 | 46,744 |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) — Overall Time | N/A | 9.024 s | N/A | N/A | 6.883 s | 5.348 s |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) — Image Generation Speed | N/A | 1.128 s/image | N/A | N/A | 0.860 s/image | 0.669 s/image |
| Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) — Overall Score | 1,124 | 1,940 | 1,805 | 2,010 | 2,473 | 3,352 |
| Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) — Overall Time | 533.736 s | 326.550 s | 332.400 s | 298.499 s | 242.606 s | 178.946 s |
| Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) — Image Generation Speed | 33.359 s/image | 20.409 s/image | 20.775 s/image | 18.656 s/image | 15.163 s/image | 11.184 s/image |
Luxmark
Luxmark is a GPU benchmark that utilizes LuxRender, an open-source ray-tracing renderer, to assess a system’s performance in handling highly detailed 3D scenes. This benchmark is particularly relevant for evaluating the graphical rendering capabilities of servers and workstations, especially in visual effects and architectural visualization applications, where accurate light simulation is crucial.
In Luxmark, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT scored 4,220 in the Food scene and 8,007 in the Hall scene. These results place it below the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti, which achieved scores of 6,590 and 15,348 in the same tests. AMD’s RX 9070 and 9070 XT showed incremental improvements, with scores of 8,233 and 8,610 in the Food scene and 16,566 and 16,758 in the Hall scene, respectively. NVIDIA’s RTX 5070 FE extended the lead further at 9,061 and 22,062, while the ASUS PRIME RTX 5070 Ti dominated both tests with scores of 12,073 and 28,635. This positions the RX 9060 XT as a lower mid-range performer in ray-traced rendering tasks, trailing notably behind both AMD’s upper-tier cards and NVIDIA’s 5070-class GPUs, especially in more complex scenes like Hall.
| Luxmark (higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 FE | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 Ti |
| Food Score | 4,220 | 6,590 | 8,233 | 8,610 | 9,061 | 12,073 |
| Hall Score | 8,007 | 15,348 | 16,566 | 16,758 | 22,062 | 28,635 |
Geekbench 6
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures overall system performance. The Geekbench Browser allows you to compare any system to it.
In Geekbench 6, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT achieved an OpenCL score of 102,750, placing it firmly in the lower tier of the tested GPUs. It was outperformed by AMD’s own RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT, which scored 138,463 and 188,892, respectively. NVIDIA’s RTX 5060 Ti posted a higher result at 150,743, while the RTX 5070 FE came in even stronger at 173,255. The highest score was delivered by the ASUS PRIME RTX 5070 Ti, which reached 246,875. These results indicate that while the RX 9060 XT is adequate for general-purpose GPU compute tasks, it significantly lags both NVIDIA’s mid-range cards and AMD’s higher-tier offerings in raw OpenCL performance.
| Geekbench (higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 FE | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 Ti |
| GPU OpenCL Score | 102,750 | 138,463 | 150,743 | 173,255 | 188,892 | 246,875 |
3D Mark
3DMark Port Royal, Speed Way, and Steel Nomad are GPU benchmarks that test performance in different scenarios. Port Royal focuses on ray tracing, Speed Way evaluates performance in racing simulations, and Steel Nomad challenges GPUs with high-intensity, realistic graphics. They assess GPU capabilities in rendering, lighting, and dynamic scenes.
In 3DMark Port Royal, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT scored 9,751, coming in below the RTX 5060 Ti at 10,432 and significantly behind the RTX 5070 FE at 14,026. The RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT posted stronger results with 15,760 and 17,989, while the ASUS PRIME RTX 5070 Ti led with 19,290. In Speed Way, the RX 9060 XT reached 3,004, trailing all other GPUs tested. The RTX 5060 Ti scored 4,184, the RX 9070 hit 5,791, and the RX 9070 XT pushed to 6,237. The RTX 5070 FE came in at 5,869, and the RTX 5070 Ti again topped the list at 7,709. For Steel Nomad, the RX 9060 XT achieved 3,767, slightly ahead of the RTX 5060 Ti’s 3,611 but well behind the RTX 5070 FE at 5,019. AMD’s RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT scored 5,992 and 6,977, while the 5070 Ti landed at 6,458. These results consistently position the RX 9060 XT behind both its higher-end AMD counterparts and NVIDIA’s mid-to-upper-tier offerings.
| 3D Mark (higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 FE | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 Ti |
| Port Royal | 9,751 | 10,432 | 14,026 | 15,760 | 17,989 | 19,290 |
| Speed Way | 3,004 | 4,184 | 5,869 | 5,791 | 6,237 | 7,709 |
| Steel Nomad | 3,767 | 3,611 | 5,019 | 5,992 | 6,977 | 6,458 |
Power Consumption: Gigabyte Radeon RX 9060 XT
Power consumption is a significant component of any high or low-end computing platform. Each new generation of GPU consumes more power under load, meaning larger power supplies and ample airflow for cooling. However, there is another aspect to power regarding performance: faster GPUs might spike higher, but the duration of each workload decreases.
We tested the Gigabyte AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT power draw, which has a 160W TDP rating. During the Procyon AI image-generation test, power consumption rose from 148W at idle to 610W under load, a system increase of 462W. The average power draw under load was approximately 439W. Total system load is significantly higher than the entry NVIDIA models during the same period.
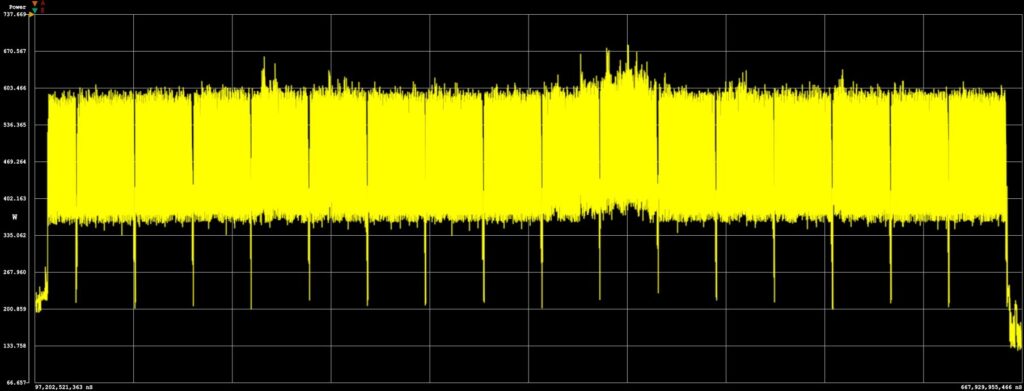
The second-to-last image was generated in just 33 seconds, with the system consuming 4 Wh during that period.
| Power Testing Summary |
AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | PNY NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 FE | ASUS Prime NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5070 Ti |
| Power Consumed | 4 Wh | 3.41Wh | 2.13 Wh | 2.46Wh | 1.66Wh |
| Test Duration | 33 s | 17.4 s | 20.2 s | 19.2 s | 11.1 s |
Conclusion
The Gigabyte AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT delivers solid 1080p and 1440p gaming performance at one of the most affordable price points in its class. Gigabyte’s GAMING OC 16G model adds efficient cooling and a well-built design that complements the card’s focus on thermal and acoustic performance. For gamers looking to play modern titles at high settings without stretching their budget, it’s a practical and capable choice.
However, in AI and compute workloads, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT appears to have limitations. While it’s capable of handling lighter inference tasks and small-scale acceleration, it struggles to keep up in more demanding scenarios, as shown in testing with text generation or intensive image generation. For users with occasional AI needs, it’s not a good fit; they should consider upgrading to a higher tier for stronger performance.
However, for gaming-first users who prioritize price, efficiency, and modern display support, the AMD Radeon RX 9060 XT meets the mark with its 16GB variant, priced under $400 at $379, and the 8GB version available for just $299. It brings RDNA 4’s architectural improvements to the mainstream crowd and offers a compelling balance of performance and cost for beginners.




 Amazon
Amazon