AMD’s acquisition of Enosemi is a strategic move aimed at accelerating AMD’s capabilities in silicon photonics and co-packaged optics, especially for next-generation AI systems.
Who is Enosemi?
Enosemi is a Silicon Valley-based startup founded in 2023 by Ari Novack and Matthew Streshinsky, both with strong backgrounds in semiconductor engineering. The company specializes in photonic integrated circuits, microchips that use light (photons) instead of electricity to transmit data. Their products include optical interconnects, which are essential for integrating computing and networking components within data centers. Before the acquisition, Enosemi had only 16 employees and had raised $150,000 in venture funding. Their expertise lies in building and shipping photonic integrated circuits at scale, a rare capability among startups in this space.
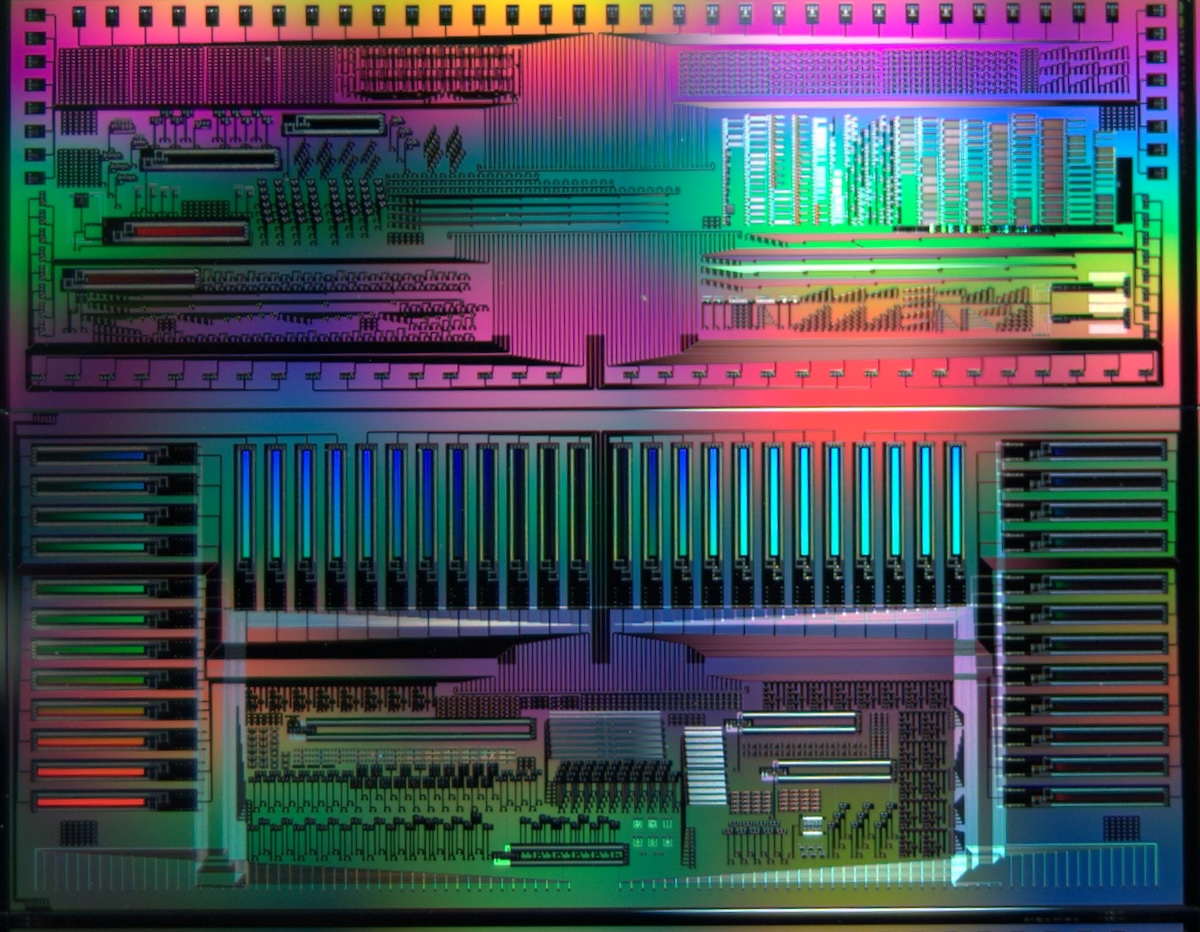
Enosemi products include chiplets, custom silicon, IP products, and photonic subsystems.
What’s the End Game?
The acquisition helps AMD scale its ability to deliver advanced photonics and co-packaged optics solutions, which are becoming increasingly important as AI models expand and demand faster, more efficient data movement. Co-packaged optics can provide higher bandwidth density and improved power efficiency compared to traditional approaches. This represents a transformative step in system architecture, with tighter integration between compute and networking to support the performance and scale that advanced AI workloads require. Silicon photonics is regarded as a crucial technology for addressing the bandwidth and energy constraints of traditional electrical interconnects in data centers and AI hardware.
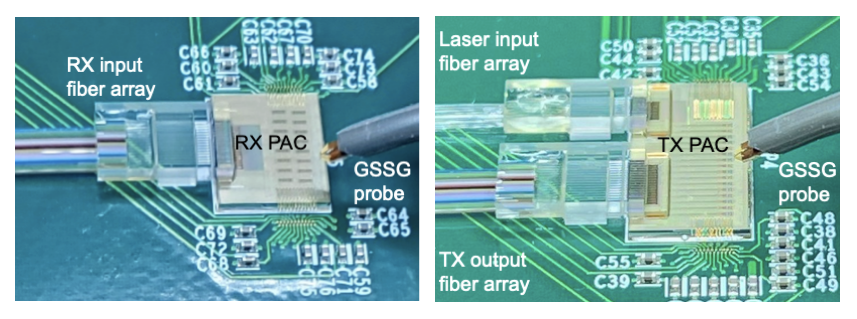
Enosemi has been collaborating with AMD as an external development partner, and this acquisition formalizes and strengthens that relationship. According to Brian Amick, AMD’s SVP of technology and engineering, Enosemi’s team will help AMD “immediately scale our ability to support and develop various photonics and co-packaged optics solutions across next-gen AI systems.”
What’s the Strategy?
It should come as no surprise that AMD is focused on beefing up its photonics advancements. The company is laser-focused on taking some of NVIDIA’s market share in the data movement and networking sector. Although NVIDIA leads the pack in AI compute and is expanding its networking portfolio, AMD is catching up with acquisitions like Enosemi, which closes the gap and provides a more comprehensive, high-performance stack.
Both AMD, with the Enosemi acquisition, and NVIDIA, with its silicon photonics switch, are betting on silicon photonics as the backbone of next-generation AI and data center infrastructure. They are converging on similar solutions, including co-packaged optics, photonic interconnects, and high-bandwidth switches, to solve the problem of moving massive amounts of data, keeping pace with the demands of modern AI.
AMD has built a comprehensive portfolio that addresses the rapidly evolving needs of AI, from foundational silicon to systems-level integration. That journey has included integrating Xilinx’s AI Engines and adaptive SoC technologies, adding advanced data movement and networking capabilities through Pensando, building a top-notch software team with the additions of Silo AI and Mipsology. It also includes scaling full rack-level system design with the latest acquisition of ZT Systems.
These acquisitions reflect AMD’s strategy of building a full-stack, future-proof data center business by acquiring specialized technology and talent. Pensando gave AMD a foothold in smart networking and DPUs, while Enosemi is about owning the next wave of high-speed, photonics-based interconnects for AI and HPC. AMD and other chipmakers are working diligently to meet the increasing demands of larger AI models, as the bottleneck shifts from computing power to data movement and interconnect bandwidth.
AMD wasted no time integrating the new team. Enosemi’s co-founder, Ari Novack, is now listed as a silicon design engineering fellow at AMD. This signifies that the core technical team is being retained and integrated into AMD’s engineering organization.
Although the financial terms of the acquisition were not disclosed, considering Enosemi’s size and limited funding, this was likely a talent and technology acquisition rather than a significant financial outlay.
Bottom line
AMD’s acquisition of Enosemi focuses on acquiring a nimble, highly skilled team with proven expertise in photonic integrated circuits. Moreover, this talent is essential for enhancing AMD’s roadmap for AI-optimized hardware, particularly in terms of high-speed, energy-efficient data movement within data centers.
AMD has built a comprehensive portfolio that addresses the rapidly evolving needs of AI, from foundational silicon to systems-level integration. That journey has included integrating Xilinx’s industry-leading AI Engines and adaptive SoC technologies, adding advanced data movement and networking capabilities through Pensando, building a world-class software team with the additions of Silo AI and Mipsology. It also includes scaling full rack-level system design with the latest acquisition of ZT Systems.




 Amazon
Amazon