IBM has introduced Granite 4.0, a new generation of open-weight language models engineered to run faster, more cost-effectively, and with stronger governance than conventional AI systems. Rather than chasing trillion-parameter scale, Granite 4.0 prioritizes efficiency, control, and predictable performance, criteria that matter most when moving from AI pilots to production at enterprise scale. Notably, Granite 4.0 is the first open-weight model family to earn ISO 42001 certification for responsible AI management, signaling a push to make open models viable for regulated and security-conscious environments.

Kate Soule, who leads Technical Product Management for IBM’s AI models portfolio, characterized Granite 4.0 as pragmatic building blocks for enterprise workloads. In essence, reliable models that scale to production, lower agent run costs, and reduce the friction associated with broader deployments.
Rethinking AI Architecture for Real-World Scale
The market has trended toward ever-larger frontier models from OpenAI, Meta, and Mistral. IBM’s counterpoint is that most businesses, especially those running multi-tenant, policy-heavy environments, prioritize utilization, governance, and operational reliability over sheer size. Granite 4.0 centers on a hybrid architecture that combines transformer layers with Mamba-2, a newer sequence model.
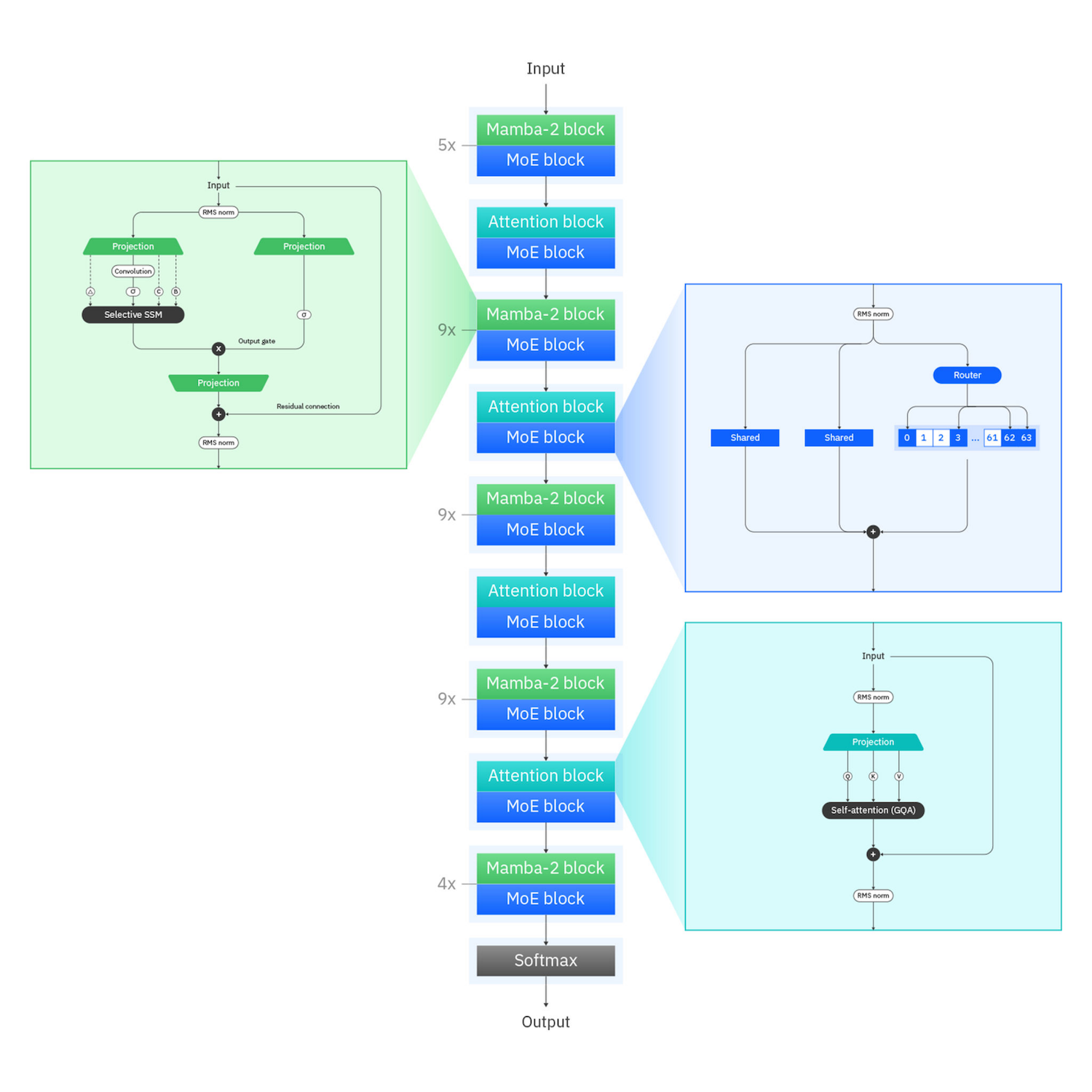
- Why this matters: Transformers deliver strong quality, but their compute and memory scale roughly with the square of context length, making long documents and many concurrent sessions expensive. Mamba-2 scales linearly with sequence length, dramatically reducing memory pressure.
- The result: IBM reports 70–80% lower memory usage compared to transformer-only models, while maintaining competitive throughput and quality. For teams graduating from proofs of concept, this can be the difference between an attractive demo and a production-ready service with sustainable unit economics.
Soule framed the hybrid approach as a direct response to enterprise pain points: pilots frequently rely on massive models that prove too costly or too brittle at rollout. Granite 4.0 is designed to maintain high performance while reducing the hardware footprint and operating costs.
A Family of Models Tuned for Enterprise and Edge
Granite 4.0 ships as a portfolio targeting diverse deployment profiles—from data center inference clusters to edge devices:
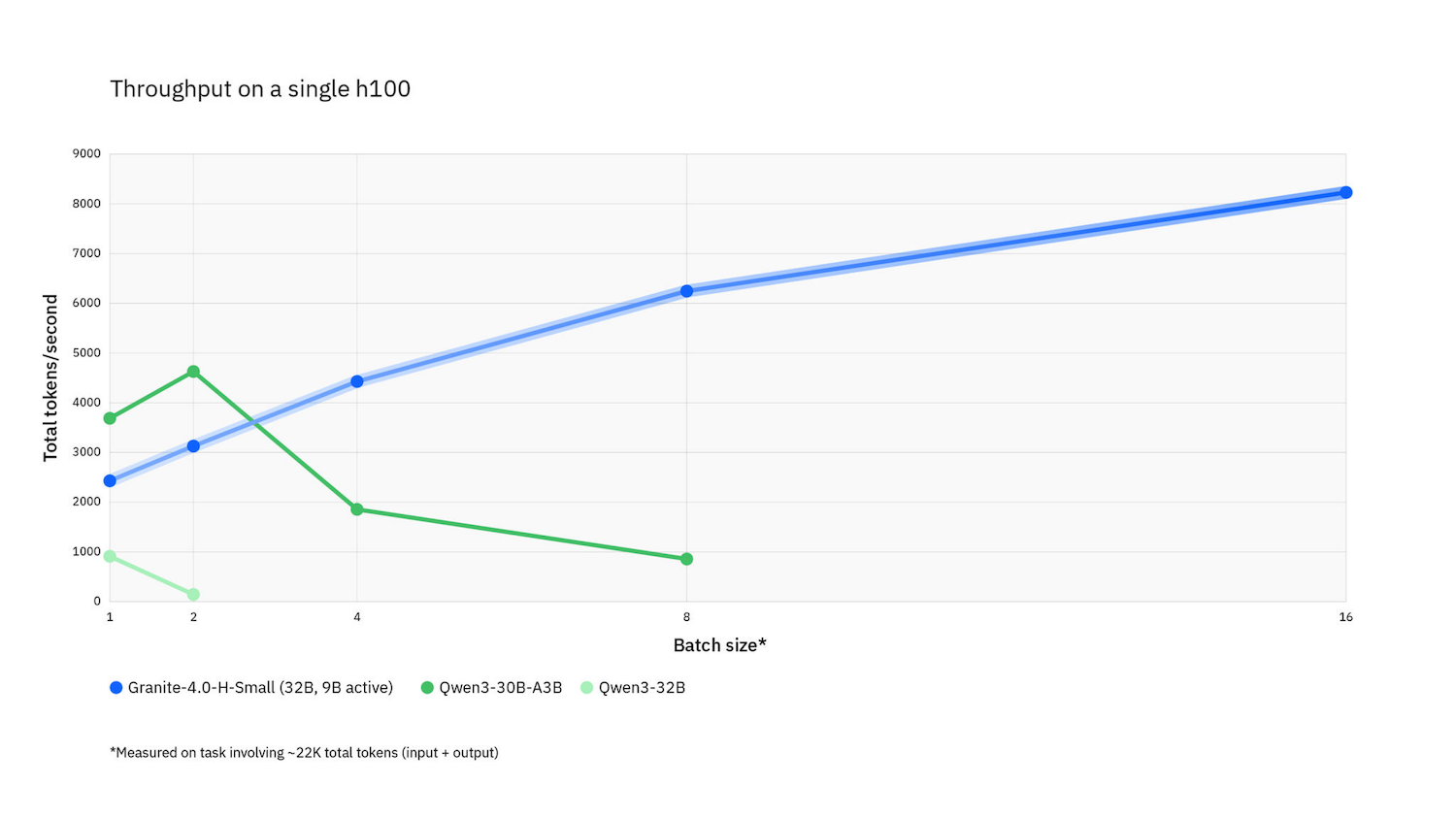
- Granite-4.0-H-Small (hybrid, mixture-of-experts): 32B parameters with ~9B active per token. Positioned as a workhorse for enterprise automations, including customer support, RAG pipelines, and multi-tool agents that require consistent latency and policy compliance.
- Granite-4.0-H-Tiny: 7B parameters with ~1B active.
- Granite-4.0-H-Micro: 3B parameters. These are designed for edge scenarios and task-specific agents where fast spin-up, modest memory requirements, and predictable inference costs are crucial.
- Granite-4.0-Micro: 3B dense model with a conventional attention-driven transformer architecture to accommodate platforms and communities that do not yet support hybrid architectures.
- Granite-4.0-D-3B (dense transformer): A conventional transformer-only option for teams favoring standard architectures and tooling compatibility.
|
Granite-H-Small |
Granite-H-Tiny |
Granite-H-Micro |
Granite-Micro |
|
| Architecture Type | Hybrid, Mixture of Experts | Hybrid, Mixture of Experts | Hybrid, Dense | Traditional, Dense |
| Model Size | 32B total parameters
9B activated parameters |
7B total parameters
1B activated parameters |
3B total parameters | 3B total parameters |
| Intended Use | Workhorse model for key enterprise tasks like RAG and agents | Designed for low latency, edge, and local applications, and as a building block to perform key tasks (like function calling) quickly within agentic workflows | Designed for low latency, edge, and local applications, and as a building block to perform key tasks (like function calling) quickly within agentic workflows | Alternative option for users when Mamba2 support is not yet optimized (e.g. llama.cpp, PEFT, etc) |
| Memory Requirements (8-bit) | 33 GB | 8 GB | 4 GB | 9 GB |
| Example Hardware | NVIDIA L4OS | RTX 3060 12GB | Raspberry-Pi 8GB | RTX 3060 12GB |
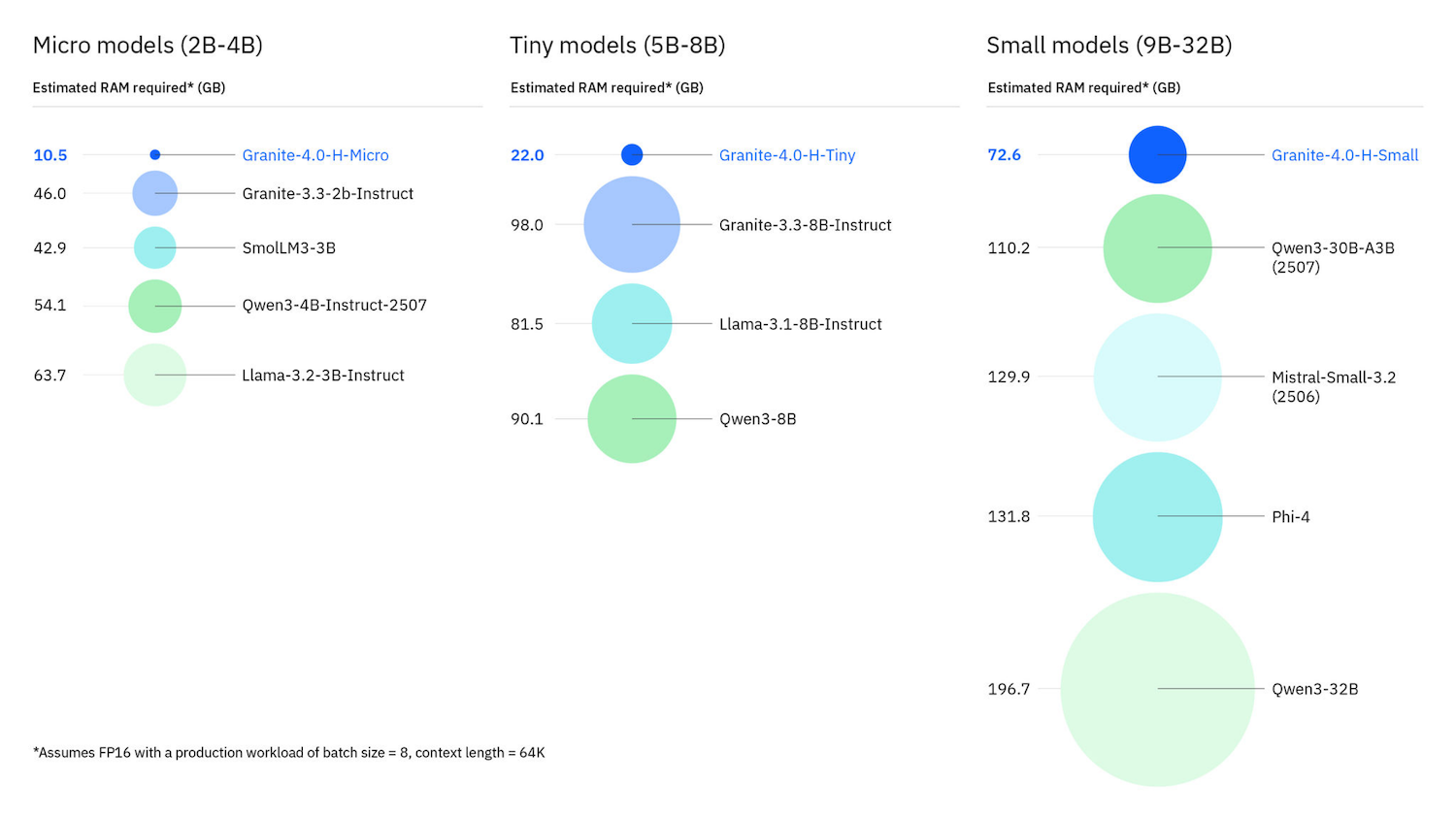
IBM highlights practical footprint gains, such as the 3B-parameter model with a 128K-token context, which runs at 8-bit precision and can fit in roughly 4GB of memory. It’s light enough for developer laptops and even constrained devices like the Raspberry Pi. IBM also plans “Nano” variants with fewer than 300M parameters to expand the addressable edge.
The portfolio strategy is straightforward, providing developers with customizability and lightweight solutions that facilitate rapid iteration, while offering executives clear markers of trust, governance, and operational readiness.
Building Trust into Open Models
Granite 4.0 is positioned to differentiate on governance as much as on efficiency:
- ISO 42001 for responsible AI: Granite is the first open-weight model family to earn this certification, following an external audit of IBM’s training, testing, and data governance processes. For many buyers, this establishes a compliance baseline for adopting open models in sensitive environments.
- Cryptographic signing: All Granite 4.0 checkpoints on Hugging Face are cryptographically signed to verify provenance and integrity, reducing supply-chain risk.
- Coordinated security model: IBM launched a bug bounty program with HackerOne to encourage external testing and responsible disclosure around model vulnerabilities and safety issues.
Enterprises have long balanced the flexibility of open source against concerns around security and accountability. IBM’s stance is that ISO certification, verifiable artifacts, and incentivized testing together raise confidence that open-weight models can be safely operationalized without sacrificing control.
Technical Assessments
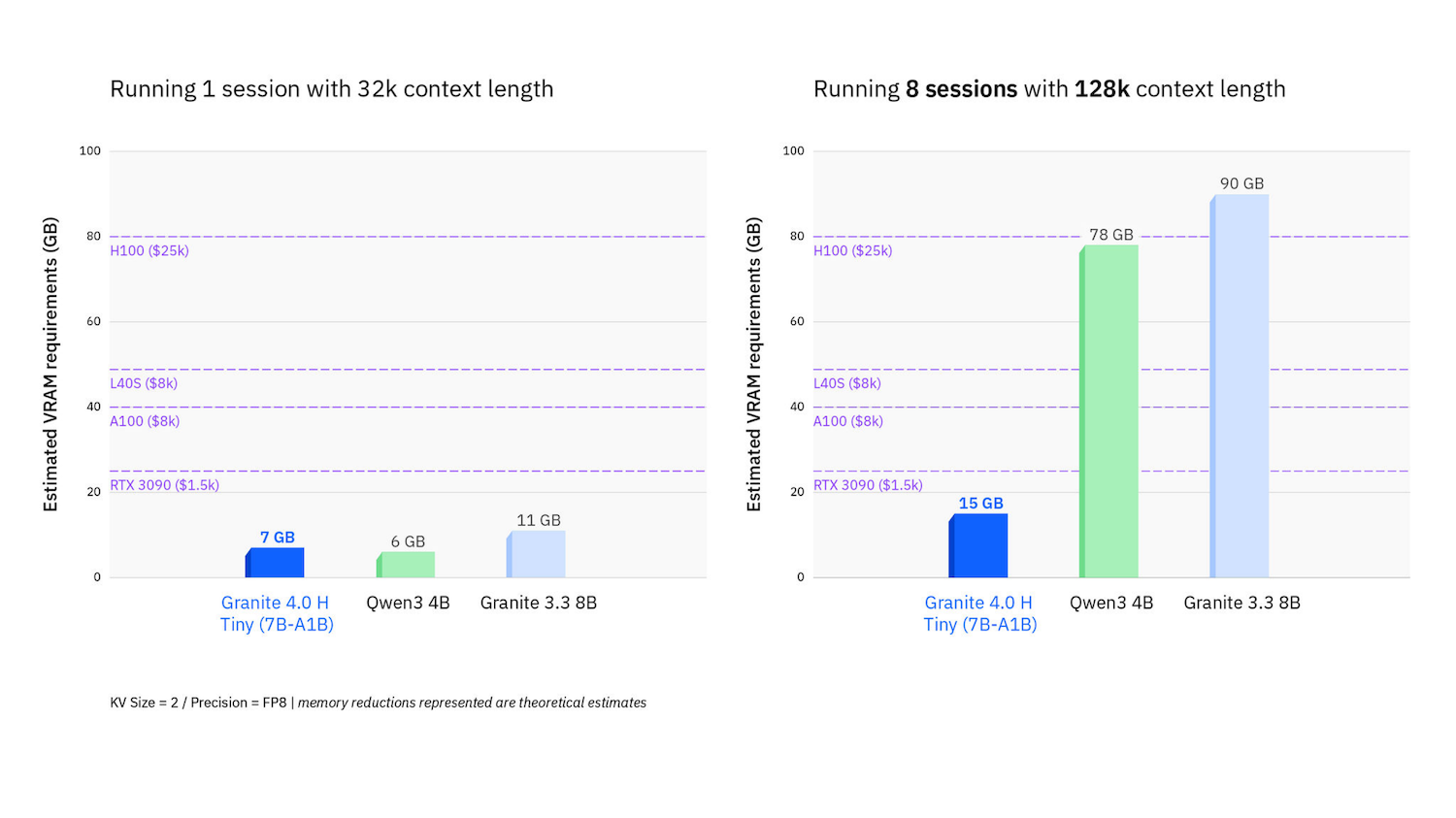
- Memory and TCO profile: The hybrid transformer + Mamba-2 approach can compress memory budgets by 70–80% versus transformer-only peers, enabling higher concurrency and reduced infra costs for the same SLA.
- Agent economics: Lower per-token and per-session costs can materially change the feasibility of agent-based automations and RAG systems, especially when context windows extend to 128K tokens or more.
- Governance baseline: ISO 42001, along with signed checkpoints and a public bounty program, contributes to an auditable posture for procurement, risk, and compliance teams.
- Deployment breadth: From 32B MoE to 3B dense and sub-1B Nano plans, the range supports everything from data center orchestration to edge inference, with a path to unify dev/test/prod stacks on smaller, more efficient models.
Impact
Granite 4.0 signals IBM’s efficiency-first approach in enterprise AI, featuring open weights with production guardrails, a hybrid architecture optimized for long-context workloads and multi-agent orchestration, and a certification-led approach to trust. For organizations prioritizing governed deployments, predictable latency, and sustainable cost-to-serve, Granite 4.0 offers a practical alternative to giant frontier models, built to scale.




 Amazon
Amazon