OpenNebula has released version 7.0 “Phoenix,” marking a significant leap forward for organizations building sovereign, AI-ready, and edge-enabled cloud environments. This major update delivers substantial advancements in storage, automation, hybrid multi-cloud integration, and GPU-accelerated AI workloads, positioning OpenNebula as a compelling, future-ready alternative to traditional virtualization platforms.

A key focus of OpenNebula 7.0 is simplifying the migration process for organizations moving away from VMware. The new release introduces AI-powered Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), native integration with NetApp’s iSCSI and Veeam backup solutions, a completely redesigned LVM backend, and support for importing OVA files. These features collectively streamline and accelerate the transition to OpenNebula, reducing complexity and risk.
Upgraded Storage Management
Storage management receives a notable upgrade in this release. Automated NFS mount configuration makes shared storage easier to manage, while a complete rewrite of the local datastore backend enhances performance and supports modern disk operations. OpenNebula 7.0 also introduces full backup support for LVM datastores and incremental backups for Ceph, laying the foundation for robust, enterprise-grade backup strategies.
OpenNebula 7.0 introduces OneDRS, an AI-powered alternative to VMware DRS, aimed at improving infrastructure efficiency and reducing costs. OneDRS features predictive scheduling, customizable levels of automation, and flexible migration thresholds. When paired with the new time series monitoring framework, OneDRS enhances capacity planning and allows for quicker responses to changing usage patterns.
Resource governance is enhanced with the introduction of cluster-level quotas, which provide administrators with precise control over resource allocation. This feature is handy in edge and multi-tenant environments. Additionally, the introduction of Generic Quotas enables organizations to monitor custom resources, such as virtual GPUs (vGPUs) or software licenses, allowing for customized governance tailored to advanced workloads.
PCI Passthrough and vGPU Support
OpenNebula 7.0 delivers significant improvements for AI and HPC applications, including enhanced PCI passthrough and full support for NVIDIA-mediated vGPU devices. GPU resource allocation is now more flexible and scalable, with vGPU profiles and PCI devices configurable at the host and cluster levels, enabling fine-grained control across heterogeneous hardware environments.
The appliance catalog has also been updated. The Ray Appliance now features vLLM support, OpenAPI compatibility, Hugging Face integration, model quantization, and multi-GPU configurations. These capabilities have been extended to the NVIDIA Dynamo Appliance, providing teams with a solid foundation for running production-grade inference workloads. OpenNebula 7.0 also integrates with NVIDIA NIM and introduces advanced features for building isolated networks using BlueField-3 DPUs.
Hybrid provisioning receives foundational improvements in this release, preparing users for distributed cloud strategies. While a complete redesign of the provisioning engine is planned for a future maintenance release, version 7.0 already includes internal updates that expand support for additional cloud providers and simplify cluster setup. Official ARM-based architecture support is now available, with packages and Marketplace appliances for the aarch64 ecosystem.
Updated Sunstone GUI
Usability enhancements are a hallmark of OpenNebula 7.0. The Sunstone GUI has been updated to enhance accessibility, improve navigation, and provide more precise data visualization. A new cloud view offers end users real-time performance metrics and easy access to key actions. At the same time, developers can leverage Dynamic Tabs to integrate third-party tools directly into the interface. Additional improvements include enhanced security and performance for VNC access, better rendering of user inputs during appliance import, and the introduction of VM Template Profiles to simplify provisioning with predefined configurations.
Kubernetes integration is also strengthened, with updated support for Windows guest operations and the introduction of the CAPI/Rancher Appliance for RKE2 cluster management. Users can now deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters through Rancher’s UI using OpenNebula’s Cluster API implementation.
On the networking front, transparent proxying simplifies access to external services such as OneGate, and VLAN filtering streamlines tenant isolation when using Linux bridge-based networking.
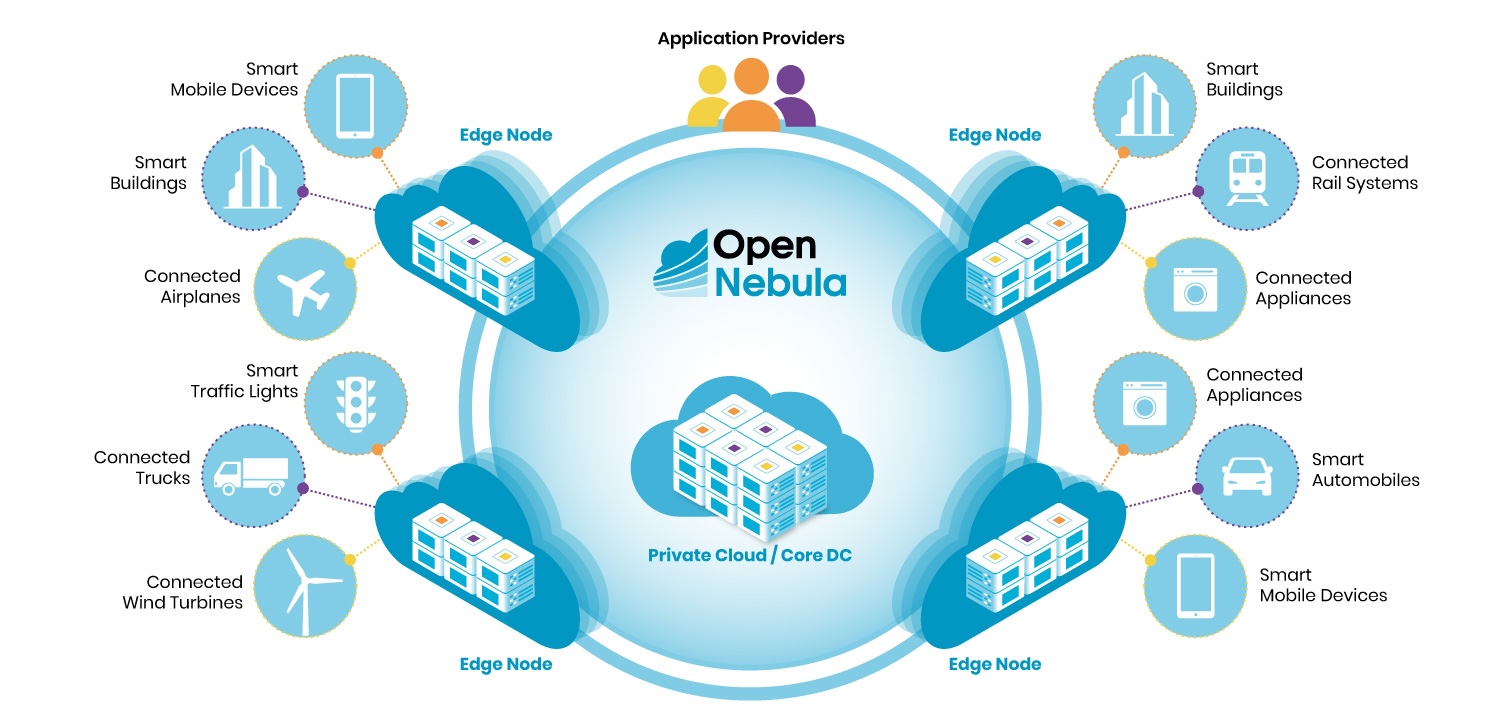
To further support adoption, OpenNebula 7.0 includes migrator packages for seamless upgrades from version 6.10, making it easier for community users to stay current and benefit from the latest innovations. Enterprise Edition subscribers continue to receive additional features, including maintenance updates, long-term support (LTS) upgrades, and seamless integration with key enterprise data center components like NetApp and Veeam.
The “Phoenix” codename reflects a broader industry transformation, as organizations move beyond legacy infrastructure and vendor lock-in to embrace open, sovereign, and intelligent cloud solutions. Version 7.0 is the first in a next-generation series, featuring a redesigned cloud-edge orchestration engine that supports distributed, sovereign, and intelligent infrastructure across hybrid and multi-provider environments.
Introducing Fact8ra
In tandem with this release, OpenNebula has introduced Fact8ra, a multi-tenant AI-as-a-Service platform designed for deploying open-source large language models (LLMs) across the HPC, cloud, and telco spectrum. Fact8ra pools computing resources from eight EU member states, France, Germany, Italy, Latvia, the Netherlands, Poland, Spain, and Sweden, using open-source technologies developed in Europe. The platform delivers seamless deployment of private LLM instances, including Mistral and EuroLLM. It offers native integration with external catalogs such as Hugging Face for access to additional AI models and datasets.
Fact8ra leverages the improved NVIDIA GPU support in OpenNebula 7.0 to aggregate GPU servers from leading European cloud and 5G edge providers, including Arsys, CloudFerro, IONOS, Leaseweb, OVHcloud, Scaleway, StackScale, and Tiscali. The platform introduces an innovative federation model that combines AI infrastructure from HPC centers and EU-funded AI Factories, supporting workload portability and interoperability with supercomputing facilities across Europe. Built on a sovereign cloud stack, including OpenNebula, openSUSE, and MariaDB, Fact8ra provides a cloud-native, multi-tenant environment for AI inference and training.
By enabling easy access to public digital infrastructures for SMEs and startups, Fact8ra plays a key role in fostering the development of a European ecosystem for sovereign AI. It accelerates the technical implementation of the EU’s AI Continent Action Plan, supporting the continent’s vision for federated, open, and intelligent AI infrastructure.




 Amazon
Amazon