The Echostreams DSS320 is a redundant storage server platform, part of the DuraStreams family. The DSS320 is designed specifically for SMB verticals, integrating the LSI Syncro CS solution for HA storage access. The DSS320 supports two hot-swap compute nodes with different motherboard options to support either uniprocessor (UP) or dual processor (DP) configurations. Unlike traditional approaches to high-availability, there is no need to cluster multiple separate servers together as both nodes are housed in the same chassis in a single CiB solution.

Using LSI Syncro CS Solution, the Echostreams DSS320 becomes a true high availability converged server and storage solution. SMB and ROBO offices using DSS320 with LSI Syncro will have an HA solution that ensures they always have access to their data. This should allow businesses to have better total cost of ownership, a high performance Direct Attached Storage (DAS), and an HA with storage controller failover and RAID data protection.
The platform is designed for distribution through OEMs and is modeled around flexible customization per use case. The DSS320 3U chassis is unique in the Syncro-enabled space, it offers 16 3.5″ bays and 4 2.5″ 7mm bays, along with four hot-swappable redundant 120mm fans for cooling. Depending on motherboard and CPU configuration, the compute cluster can support up to 1TB of RAM (512GB per node). With the addition of the four “extra” 2.5″ bays, users can insert some level of flash into the configuration for caching or as a flash volume, without sacrificing HDD capacity by giving up the 3.5″ bays.
EchoStreams DuraStreams DSS320 Specifications:
- Supported CPU:
- UP: E5-2600 Xeon V2 (Ivy Bridge)
- DP: E5-2600 Xeon V2 (Ivy Bridge)
- Chipset:
- UP: Intel C600-A
- DP: Intel C602-A
- Supported RAM per node:
- UP: E5-2600 8 x 1333/1600/1866 DDR3 up to 256GB
- DP: E5-2600 16 x 133/1600/1866 DDR3 up to 512GB
- I/O Interface:
- UP: Each node has VGA, Four GigE, 2 x USB 2.0
- DP: Each node has VGA, Serial, Four GigE, 4x USB 2.0, 1x Management RJ45
- Expansion Slots:
- UP MB: 3x PCIeGen3 Expansion slots (1x for storage use) for SAS/FC/IB Host options and optional Intel dual 10Gb I/O or FDR IB/40GbE Rear I/O Module
- DP MB: onboard I/O and 5x PCIe3 x8 Expansion slots (1x slot for storage controller,1x for clustering adapter)
- Storage: 16x 3.5” and 4x 2.5” 7mm SSD 3Gbps/6Gbps SAS dual port HDD bays
- Compatible OS: Linux RedHat Enterprise 6 64bit, Suse Linux Enterprise Server 11.2 64bit, VMware ESX 4.1/ESXi4.1, Windows 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, CentOS 5.6, Ubuntu 11.10
- Server Management:
- UP version: Optional IPMI with iKVM module
- DP version: IPMI with iKVM onboard
- Cooling: 4 x Redundant 120mm hot-swap fan modules with Smart Fan Control for optimal cooling
- Power: 1+1 1200W AC/DC or -48VDC/DC high efficiency redundant power supplies
- Dimensions (LxWxH): 29”x19”x5.25”
- Environmental:
- Operating Temperature: 0°C to 35°C
- Non-Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
- Humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing
Design and Build
The Echostreams’ DSS320 is a CiB solution with two compute nodes and front-access storage in a 3U chassis. The front of the system has power and ID lights/buttons on either side for each compute node, including network activity lights, as well as 16 3.5″ HDD trays and four 2.5″ 7mm SSD trays running across the middle. Compared to other 3U CiB solutions we’ve seen that have offered just 16 3.5″ bays, EchoStreams ups the ante by including four slim 7mm SSD slots to create a more dense platform with greater storage and performance potential.
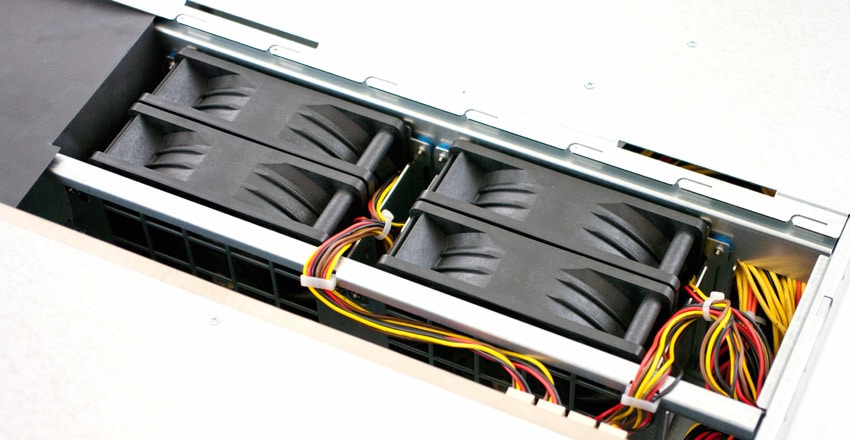
The rear of the system has access to both compute nodes with one on top of another. Redundant power supplies are located on the left side, with redundant cooling accessible from under the top cover. Along the rear of each compute node are the management ports including USB, VGA, KVM, 1GbE (iKVM) as well as twin 1GbE for network access. EchoStreams also goes a great deal further to maximize customization potential by offering 5 HHHL PCIe slots for expansion, including one internal slot dedicated to the clustered RAID card or HBA. In our configuration we have the internal slot populated with the LSI Syncro CS adapter, as well as one dual-port Mellanox ConnectX-3 40GbE card for high-speed network connectivity.

EchoStreams goes to great lengths to squeeze as much performance as possible from the DSS320, going as far as offering specialized firmware for the JBOD backplane to dedicate half the SAS channels to the SSDs and half to the HDDs. This allows the SSDs to stream data at their full bandwidth, helping in caching scenarios or those where a dedicated SSD volume is presented through shared storage.
Testing Background and Comparables
We publish an inventory of our lab environment, an overview of the lab’s networking capabilities, and other details about our testing protocols so that administrators and those responsible for equipment acquisition can fairly gauge the conditions under which we have achieved the published results. None of our reviews are paid for or overseen by the manufacturer of equipment we are testing.
We will be comparing the Echostreams’ DSS320 to the Quanta CB220, X-IO Hyper ISE 710, Dell EqualLogic PS6110XS, the Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS, and the NetApp FAS2240-2 as well as the Seagate 10k7 R10 x 16, the Seagate 6TB SAS x 16, Seagate 6TB SATA x 16, WD Se 4TB x 16, and WD RE4 SAS 3TB x 16. We configured the NetApp FAS2240-2 with 1 controller to evaluate its straight RAID6 10K HDD performance.
Each of the comparable arrays was also benchmarked with our Lenovo ThinkServer RD630 Testbed: Lenovo ThinkServer RD630
- 2 x Intel Xeon E5-2620 (2.0GHz, 15MB Cache, 6-cores)
- Intel C602 Chipset
- Memory – 16GB (2 x 8GB) 1333Mhz DDR3 Registered RDIMMs
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 64-bit, Windows Server 2012 Standard, CentOS 6.3 64-Bit
100GB Micron RealSSD P400e Boot SSD
- LSI 9211-4i SAS/SATA 6.0Gb/s HBA (For boot SSDs)
- LSI 9207-8i SAS/SATA 6.0Gb/s HBA (For benchmarking SSDs or HDDs)
- Intel X540-T2 10GbE PCIe 2.1 Adapter
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 10GbE PCIe 3.0 Adapter
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 InfiniBand PCIe 3.0 Adapter
Mellanox SX1036 10/40Gb Ethernet Switch and Hardware
- 36 40GbE Ports (Up to 64 10GbE Ports)
- QSFP splitter cables 40GbE to 4x10GbE
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 EN PCIe 3.0 Twin 10G Ethernet Adapter
For our testing in each DSS320 compute node we used:
- (2) Intel E5-2620 CPUs (2.0GHz, 6-core)
- 2 x 8GB ECC DDR3 RAM
- (1) Dual-port Mellanox ConnectX-3 40GbE network card
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard
- LSI 9271-8i Syncro CS RAID card
Storage shared across both compute nodes:
Application Performance Analysis
Our first benchmark of the Echostreams’ DSS320 is our Microsoft SQL Server OLTP Benchmark that simulates application workloads similar to those the Echostreams’ DSS320 and its comparables are designed to serve.
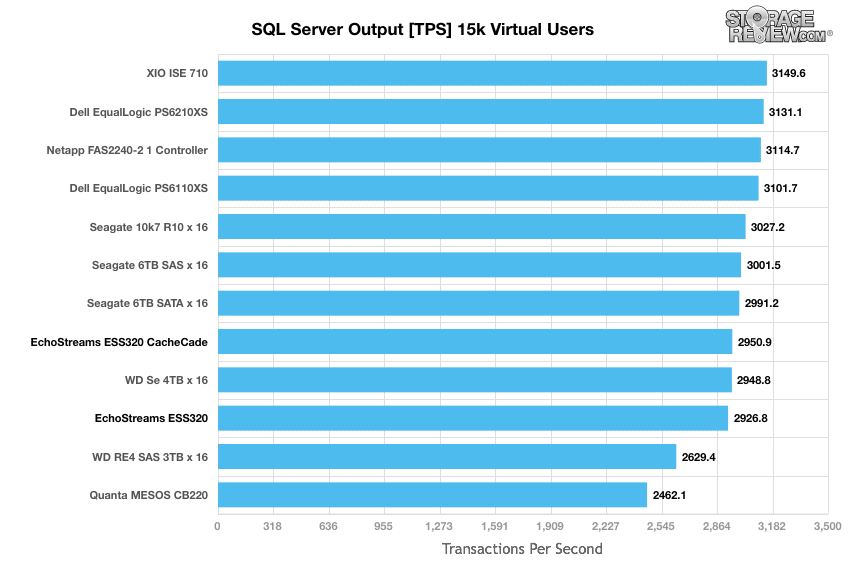
StorageReview’s Microsoft SQL Server OLTP testing protocol employs the current draft of the Transaction Processing Performance Council’s Benchmark C (TPC-C), an online transaction processing benchmark that simulates the activities found in complex application environments. The TPC-C benchmark comes closer than synthetic performance benchmarks to gauging the performance strengths and bottlenecks of storage infrastructure in database environments. Our SQL Server protocol uses a 685GB (3,000 scale) SQL Server database and measures the transactional performance and latency under a load of 15,000 virtual users.
Each of the arrays benchmarked in our SQL Server protocol is well-qualified to handle 15,000 virtual users, the DSS320 trailed behind the others coming in second to last. This isn’t bad however considering the hybrid arrays up top and the massive capacity the 6TB 7K Seagate drives offer.
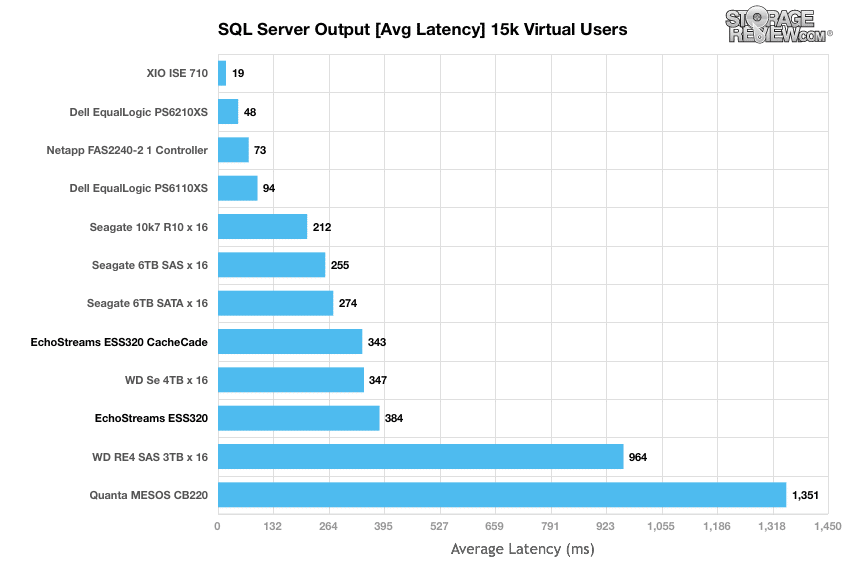
With average latency we saw a lower latency than the Quanta CB220 but higher than the drives being addressed via JBOD. The DSS320 ran with an average latency of 384ms and the cached ran with an average latency of 343ms.
Enterprise Synthetic Workload Analysis
Our enterprise storage benchmark process preconditions each device into steady-state with the same workload the device will be tested with under a load of 16 threads with an outstanding queue of 16 per thread, and then tested in set intervals in multiple thread/queue depth profiles to show performance under light and heavy usage.
- Preconditioning and Primary Steady-State Tests:
- Throughput (Read+Write IOPS Aggregate)
- Average Latency (Read+Write Latency Averaged Together)
- Max Latency (Peak Read or Write Latency)
- Latency Standard Deviation (Read+Write Standard Deviation Averaged Together)
Our Enterprise Synthetic Workload Analysis includes four profiles based on real-world tasks. These profiles have been developed to make it easier to compare to our past benchmarks as well as widely-published values such as max 4k read and write speed and 8k 70/30, which is commonly used for enterprise systems.
- 4k
- 100% Read or 100% Write
- 100% 4k
- 8K (Sequential)
- 100% Read or 100% Write
- 8k 70/30
- 70% Read, 30% Write
- 100% 8k
The Echostreams’ DSS320 with LSI Syncro CS can be useful as both SAN and NAS storage, so we established a benchmark protocol that examines the performance of the array across both scenarios in each test. Results when connecting to the Echostreams’ DSS320 with LSI Syncro CS as part of a SAN are indicated in the key by iSCSI, the protocol used to access the storage. When benchmarking NAS performance, results are indicated in the key by SMB, the protocol used for those tests.
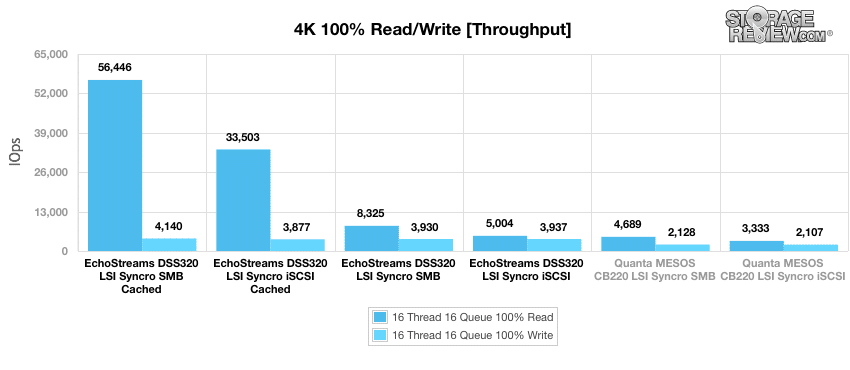
In the first workload, we measured a long sample of random 4k performance with 100% write and 100% read activity. During the random 4K throughput test we saw that the DSS320 SMB cached far out performed the others, especially with read having a read throughput of 56,446 IOPS (that is about 53,000 IOPS higher than the lowest results and about 23,000 IOPS higher than the next closest) and a write throughput of 4,140 IOPS which is only slightly higher than the non-cached SMB.
The average latency uses a large effective queue depth of 512, or 256QD. We saw somewhat similar results to the above outcome. All the DSS320 test results were much higher than the CB220 but the SMB cached again was far ahead of the others with a read latency of 4.53ms and a write latency of 61.82ms which again was only slightly better than the other write latencies.
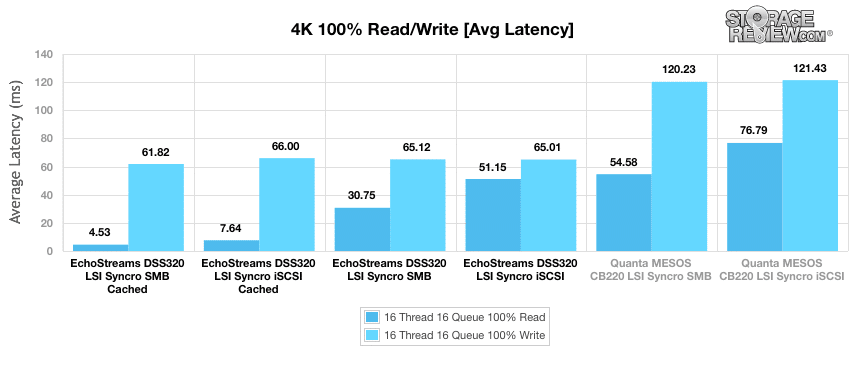
The maximum latency results reflect the worst case scenario from the 4k throughput benchmark. Once again the DSS320 SMB cached was the top performer with max read latency at 181.81ms but it fell to second in write latency behind the DSS320 iSCSI non-cached which had a write latency of 329ms.
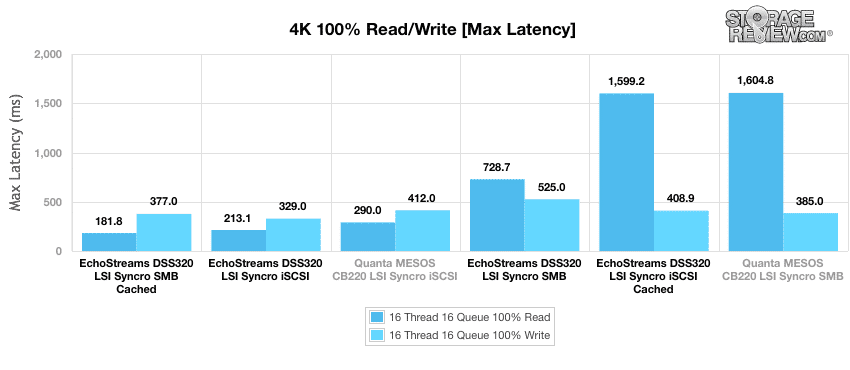
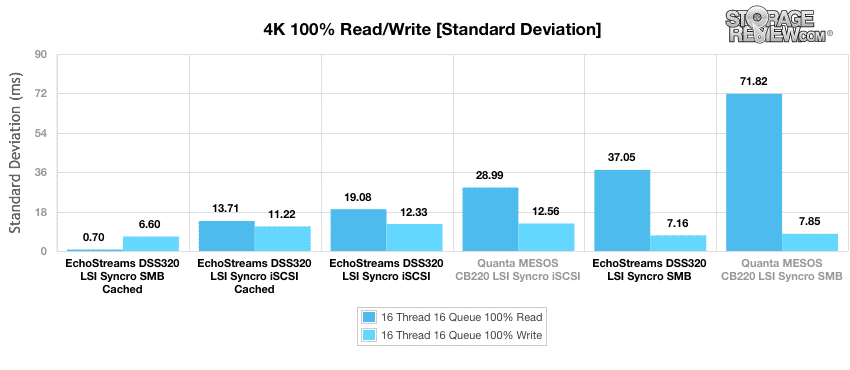
In contrast to the maximum latency report, standard deviation reflects how consistent the Echostreams’ DSS320 with LSI Syncro CS was able to maintain latency performance rather than the worst case scenario. We saw similar results to those above with the DSS320 SMB cached out performing the others with read latency of 0.698ms and write latency of 6.6ms.
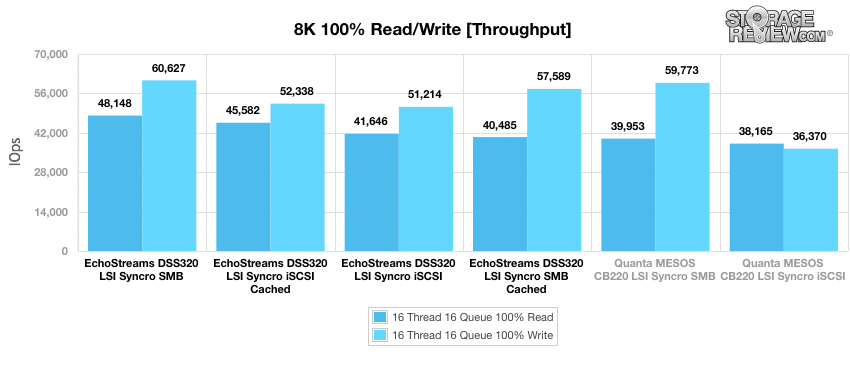
The next benchmark measures 100% 8K sequential throughput with a 16T/16Q load for 100% read and 100% write operations. This time the top performer was the DSS320 SMB non-cached with a combined performance of 60,627 IOPS write and 48,148 IOPS read.
The next synthetic enterprise benchmark measures throughput with an 8k transfer size and 70% read operations and 30% write operations. This benchmark utilizes a variety of thread and queue depth combinations from 2 threads and a queue of 2 up to 16 threads and a queue depth of 16. Similar to the 4k random throughput, the DSS320 SMB cached blew the others away taking an early lead and maintaining throughout. The DSS320 SMB cached peaked at 7,111 IOPS.
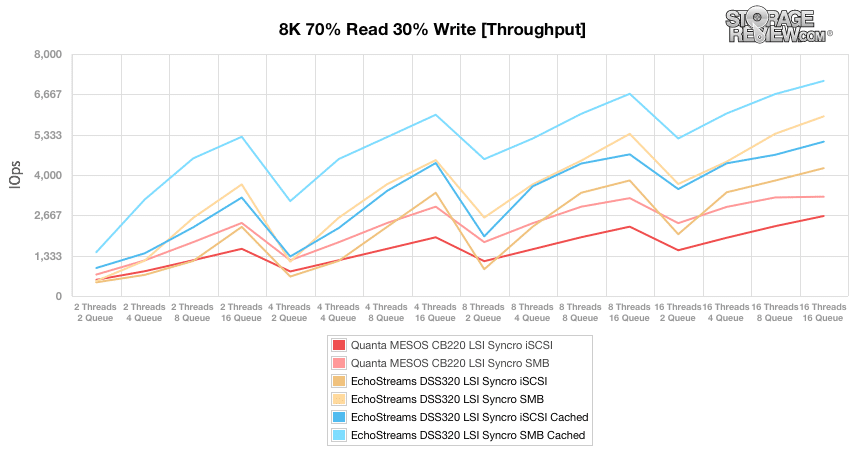
Charting the average latency in the 8k 70% read and 30% write benchmark shows similar results to the above with the DSS320 SMB cached starting off and then maintained the lead with a lower latency throughout.
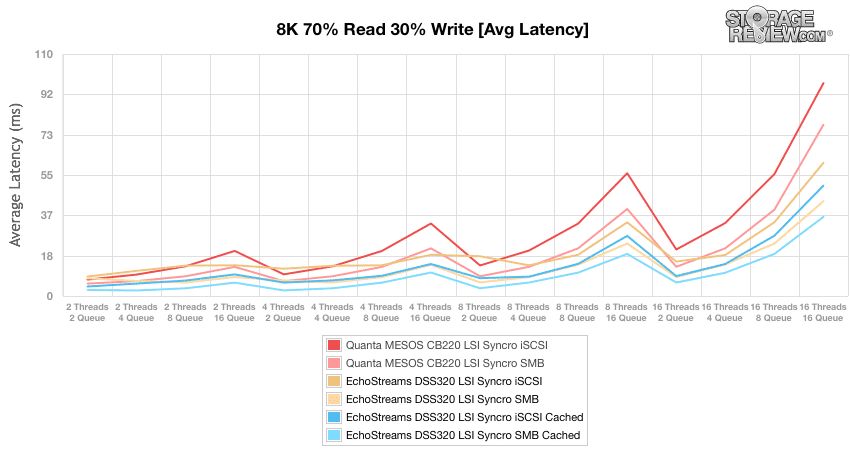
With max latency we again see a big shift in results. The DSS320 SMB cached, which had been out performing the others, had the poorest showing with higher latency for the better part of the test. The lowest latency came between the CB220 iSCSI, the DSS320 iSCSI and iSCSI cached. Overall the CB220 iSCSI had the lowest max latency taking an average of all the readings.
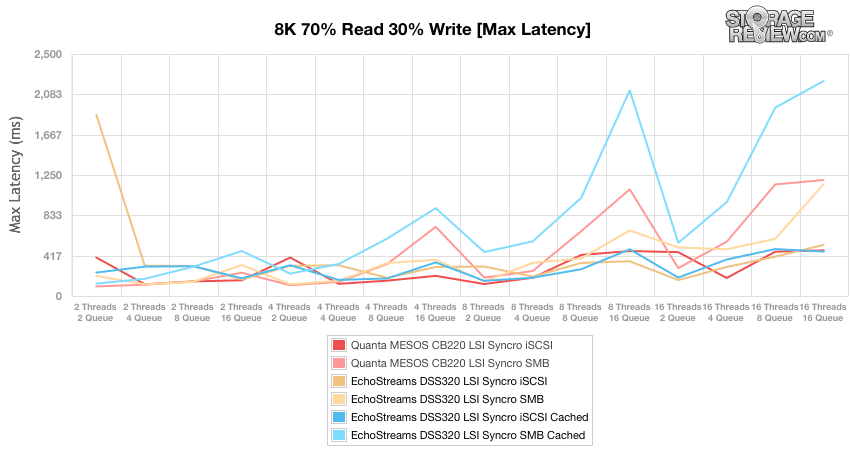
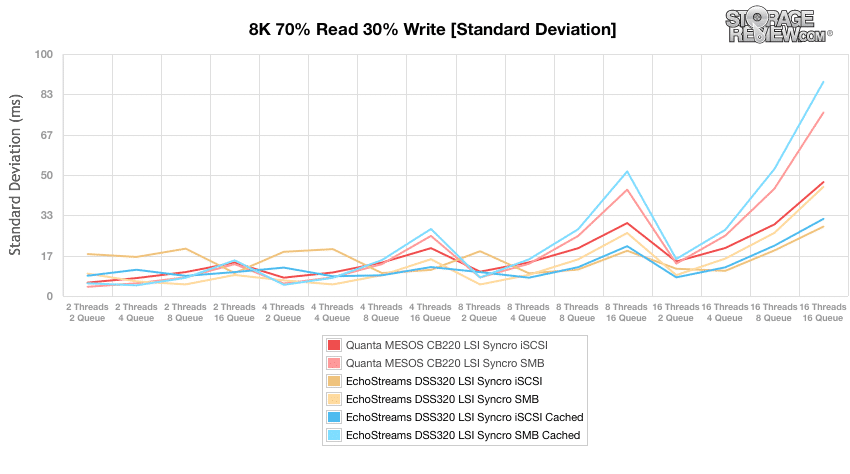
Plotting standard deviation in latency results for the 8k 70/30 benchmark showed similar results to the above but the DSS320 iSCSI cached had the lowest latency overall
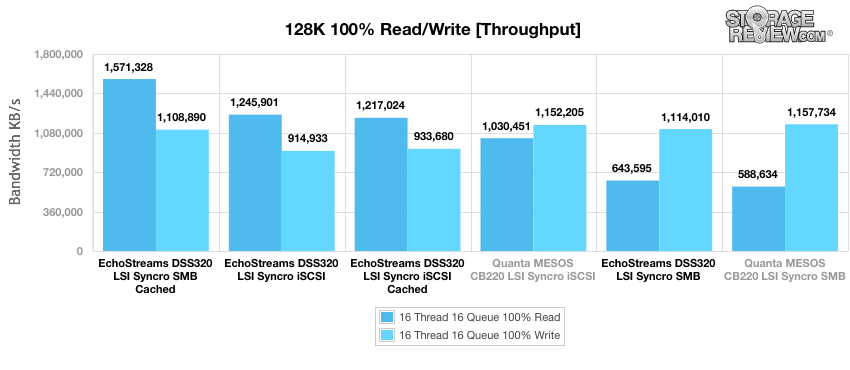
Our last benchmark measures sequential 128k transfer speed with a 16T/16Q workload on 100% read and 100% write operations. There wasn’t a tremendous difference in the write performance but the CB220 SMB had the best write performance at 1,157,734KB/s and the DSS320 SMB cached had the highest read performance at 1571328KB/s.
Conclusion
The Echostreams DuraStreams DSS320 is a highly-available storage server platform designed specifically for SMBs that want a simple and cost effective storage solution. The DSS320 offers two compute nodes configurable with up to two Intel Xeon E5-2600 Xeon V2 (Ivy Bridge) processors and can have up to 512GB of DDR3 memory. The chassis supports up to 16 3.5″ HDDs and 4 2.5″ SSDs, packing up to 96TB of raw storage with 6TB HDDs plus additional flash capacity leveraging the top four 7mm bays. The addition of LSI Syncro CS makes the DSS320 into an HA CiB, reducing downtime in businesses that require storage availability.
In our SQL Server application testing with a RAID10 configuration across 16 6TB Seagate SAS HDDs we found the DSS320 to perform fairly well sharing an iSCSI LUN to our benchmark system. Compared to a DAS environment using the same drives, the Syncro CS solution took a slight hit in latency presenting that storage over the network. With CacheCade added that gap narrowed, and would probably drop even further if the SQL Server instance was running on the cluster locally.
In terms of peak I/O in our synthetic tests we were able to pull upwards of 60k sequential IOPS write in our 8K workload over SMB, dropping to around 3,930 IOPS write with a random 4K workload also over SMB. Peak bandwidth from the DSS320 measured 1.11GB/s write over SMB and 1.57GB/s read over SMB cached. We saw a significant improvement in random read performance with our CacheCade-enabled configuration, improving 4K random read performance from 8k IOPS over SMB to over 56K IOPS. In our 8k 70/30 test was saw gains as well, with performance increasing from 65% at low thread/queue levels to 16% at high thread/queue levels. Overall the EchoStreams DuraStreams DSS320 packs a ton of storage potential into a comparatively compact 3U chassis.
Pros
- Packs up to 96TB raw in a 3U form-factor with room left over for SSD cache or volume
- Five HHHL PCIe slots available per compute node for custom configuration and expansion
- Easy to set up clustered services using Windows Failover Cluster Manager
Cons
- Some learning curve required if this is a first clustered storage product
The Bottom Line
The Echostreams DuraStreams DSS320 brings new levels of flexibility to the LSI Syncro HA storage solution, cramming 16 3.5″ bays and 4 2.5″ bays into a 3U footprint. The net result is an HA solution that’s easy to put to work with the option of adding a little bit of flash to accelerate the CiB’s performance.




 Amazon
Amazon