Inspur has released the second generation of their Solid State Drive (SSD) the NS8500, a PCIe Gen4 x4 -based enterprise controller architecture, utilizing 112L 3D eTLC NAND technology. The Inspur SSD NS8500 G2 supports NVMe 1.4 and is designed for read-intensive applications.
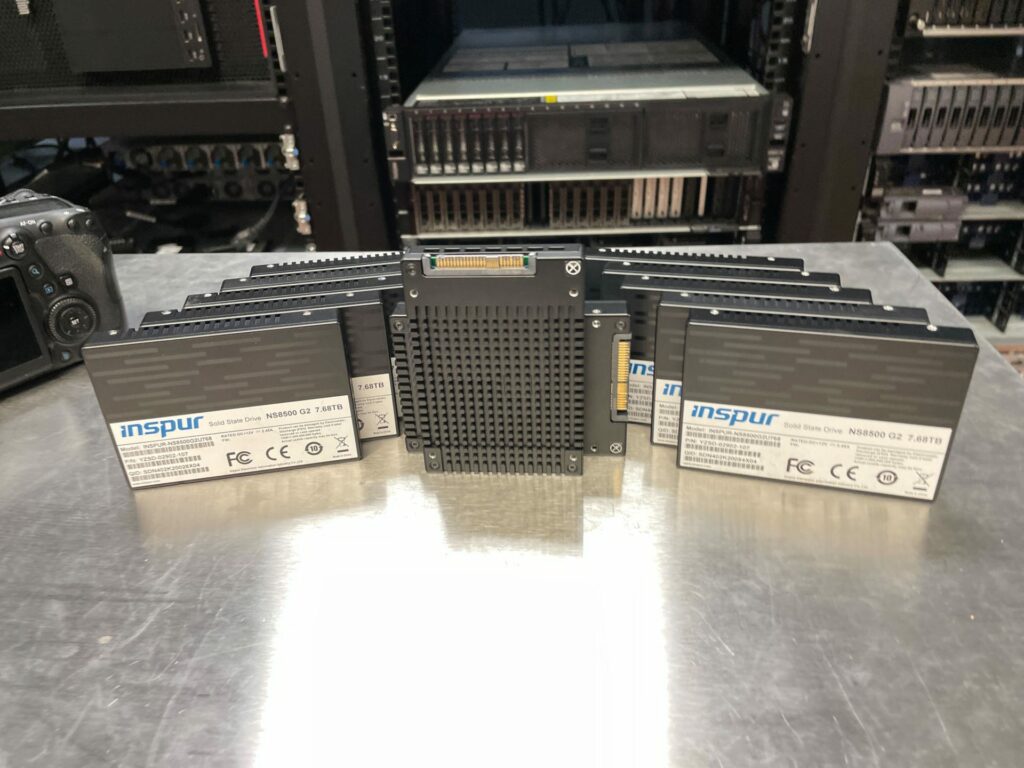

The Inspur NS8500 G2 SSD Key Advantages
The Inspur SSD NS8500 G2 SSD uses a self-developed firmware architecture and has high reliability, high stability, and high availability. Their goal is to provide high-speed and stable read-write OPS and bandwidth at extremely low latency.
The second generation controller performance is improved 100% over the first generation controller according to the company. The Inspur firmware is also developed in-house and has a multi-level power consumption design. Having control over these key components gives Inspur the opportunity to control all aspects of performance. This leads to read bandwidth of up to 7GB/s and write of up to 5GB/s. Further, the drive specifications claim 4K random read/write IOPS for more than 99% and low latency of 75/10μs.
The real MTBF is more than 2.6 million hours and is further enhanced with a strong error tolerance and correction mechanism, end-to-end data protection of full path, RAID with variable stripe, software and hardware cooperation for power loss protection, and other features. The data protection capabilities provide security and reliability from multi-level and three-dimensionality.
The NS8500 G2 also greatly improves the NAND Flash P/E (program/erase cycle), thereby extending the operational lifespan. The lifetime of the SSDs ranges from 4.36PBW at 1.92TB capacity, to 17.36PBW at 7.68TB capacity, providing a DWPD lifespan of 5 years.
Our StorageReview Youtube channel has a quick video of the 12 Inspur SSD NS8500 G2 units we received in-house.
NS8500 G2 SSD Specifications
| Form Factor | 2.5” U.2 | |||
| Host Interface | PCIe 4.0 x4 | |||
| Nand Flash | 112L 3D eTLC NAND | |||
| Performance & Capacity | Capacity | 1.92TB | 3.84TB | 7.68TB |
| Sequential Read (MB/s) | 7000MB/s | 7000MB/s | 7000MB/s | |
| Sequential Write (MB/s) | 2625MB/s | 4500MB/s | 5000MB/s | |
| 4k Random Read IOPS | 1450K | 1450K | 1600K | |
| 4k Random Write IOPS | 126K | 200K | 210K | |
| Read/Write Latency | 11us | 11us | 11us | |
| PBW | 4.34PB | 8.68PB | 17.36PB | |
| MTBF | 2,600,000 hours | |||
| Data Retention | 3 months @40°C | |||
| Operation Temp | 0°C – 70°C | |||
| Storage Temp | -40°C – 85°C | |||
| OS Support | Centos, Ubuntu, Windows, VMware, Red Hat, SUSE, Oracle Linux | |||
| Server Platform Support | NF5180M5, NF5280M5 | |||
| Product Certification | FCC/UL/CB/UNH-IOLCE/REACH/RoHS/VROC/Broadcom RAID card compatibility certification | |||
Inspur NF5280M6 Server
The server used for this review was the Inspur NF5280M6 with 1TB (32x32GB) of DDR4 memory, and 2x Intel Platinum 8360Y processors.
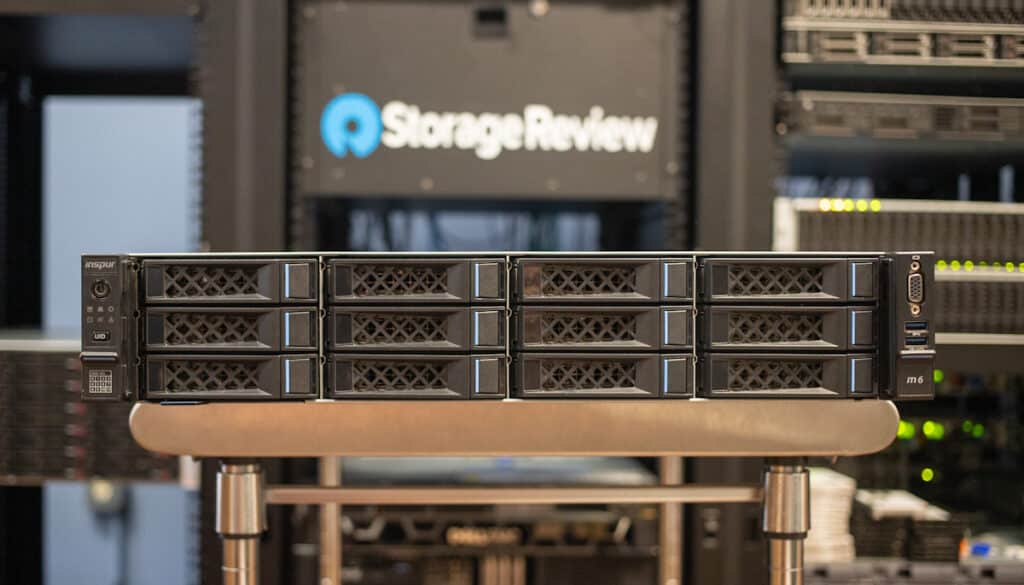


The rear and inside can also be equipped with storage bays, making it a highly versatile server for I/O intensive or storage dense workloads.
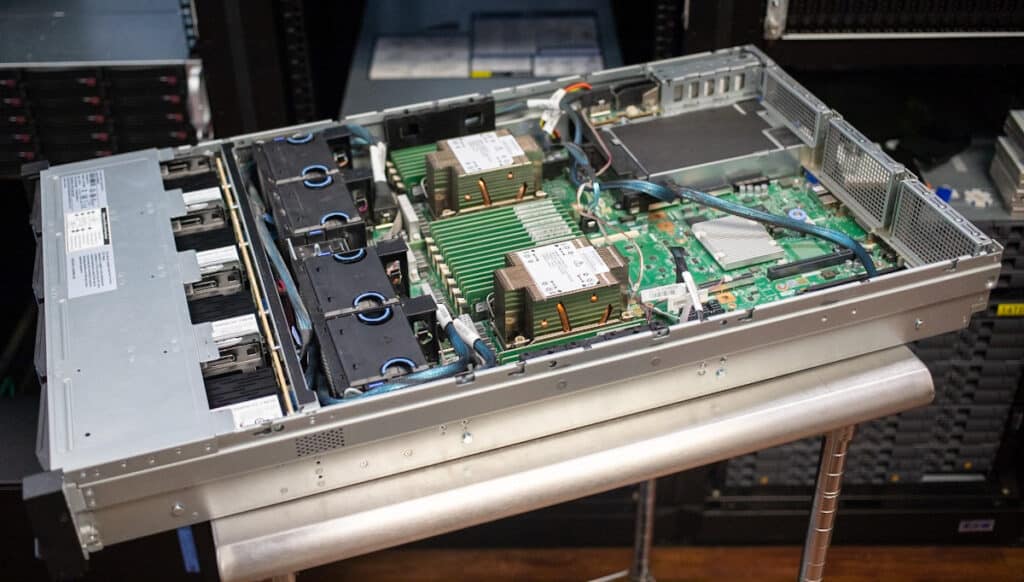

Inspur NF5280M6 Server Specifications
The detailed specifications of the Inspur NF5280M6 server appear below:
| Components | Description |
| Form Factor | 2U rack |
| Processor | Supporting 1/2 * 3rd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors |
| Max. processor core: up to 40 cores (freq. 2.3GHz) | |
| Max. processor frequency: 3.6GHz (4 cores) | |
| 3 * UPIs and each supports 11.2GT/s | |
| TDP: up to 270W | |
| Chipset | Intel® C621A |
| Memory | Up to 32 * DIMMs (8 channels /CPU, each channel supports 2 DIMMs): |
| Each CPU supports up to 16 * DIMMs, dual CPU supports 32 * DIMMs (up to 3200MT) | |
| Supporting RDIMM and BPS | |
| Memory Protection Schemes: ECC; Memory Mirroring; Memory-Level Protection | |
| Storage | Front: |
| 24 * 2.5-inch SATA/SAS/NVMe SSDs (hot swappable) | |
| 25 * 2.5-inch SATA/SAS SSDs (hot swappable) | |
| 12 * 2.5-inch/3.5-inch SATA/SAS/NVMe SSDs (hot swappable) | |
| Rear: | |
| 4 * 2.5-inch SATA/SAS/NVMe SSDs (hot swappable) | |
| 4 * 3.5-inch SATA/SAS SSDs (hot swappable) | |
| 10 * 2.5-inch SATA/SAS SSDs (hot swappable) | |
| (Optional) 2 * SATA M.2 or E1.S | |
| Internal: | |
| 4 * 3.5-inch SATA/SAS SSDs | |
| max. 2 * TF cards (1 * BIOS; 1 * BMC) | |
| Storage Controller | RAID controller, SAS controller |
| Onboard PCH supports 14 * SATA interfaces. | |
| Onboard Intel® NVMe controller, NVMe RAID Key (optional) | |
| Network | 1 * OCP3.0 (optional), 10/25/40/100/200G |
| 2 * Onboard 10G Ethernet ports | |
| Standard NICs: 1/10/25/40/100G | |
| I/O Scalable Slot | Up to 11 * PCIe slots |
| 4 * DW GPUs or 8 * SW GPUs | |
| 1 * OCP3.0 x16 NIC | |
| 1 * RAID Mezz card | |
| Interface | 2 * Rear USB3.0, 1 * Front USB3.0, 1 * Front USB2.0 |
| 1 * Front VGA | |
| 1 * Rear VGA | |
| System Fan | 4 * Hot-swappable N+1 redundancy fans |
| PSU | Supporting 2 * 550W/800W/1300W/1600W/2000W CRPS PSU, |
| 1+1 redundancy | |
| System Management | 1 * Onboard independent 1000Mbps serial port for IPMI remote management |
| OS | Microsoft Windows Server, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, CentOS, etc. |
| Dimension | with mount ears: 478.8mm (18.9 inches) x 87mm (3.5 inches) x 811.7mm (32 inches) |
| (W x H x D) | Without mount ears: 435mm (17.2 inches) x 87mm (3.5 inches) x 780mm (30.7 inches) |
| Weight | <37.5kg (82.7lbs) at highest configuration. |
| Please refer to the Technical White Paper for detail. | |
| Working Temperature | 5℃~45℃ (41℉~113℉) |
| Please refer to the Technical White Paper for detail. |
Testing Configuration
StorageReview put 12 of these new SSDs, configured as JBOD, through the paces to demonstrate how much workload an organization can get done with these in their configuration.
VDBench Workload Analysis
When it comes to benchmarking storage devices, application testing is best, and synthetic testing comes in second place. While not a perfect representation of actual workloads, synthetic tests do help to baseline storage devices with a repeatability factor that makes it easy to do an apples-to-apples comparison between competing solutions.
These workloads offer a range of different testing profiles ranging from “four corners” tests, common database transfer size tests, as well as trace captures from different VDI environments. All of these tests leverage the common VDBench workload generator, with a scripting engine to automate and capture results over a large compute testing cluster. This allows us to repeat the same workloads across a wide range of storage devices, including flash arrays and individual storage devices.
Profiles:
- 64K Sequential Read: 100% Read, 32 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 64K Sequential Write: 100% Write, 16 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 4K Random Read: 100% Read, 128 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 4K Random Write: 100% Write, 128 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 4k Mixed: 70% Read, 30% Write, 128 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 4k Mixed: 90% Read, 10% Write, 128 threads, 0-120% iorate
- Synthetic Database: SQL and Oracle
- VDI Full Clone and Linked Clone Traces
Sequential I/O Throughput
The 64k sequential reads and writes show some pretty good numbers. The 12 NS8500 G2 drives achieved over 61.6GB/s at around 384µs latency on 64k sequential reads, offering an immense amount of bandwidth for data-rich applications.
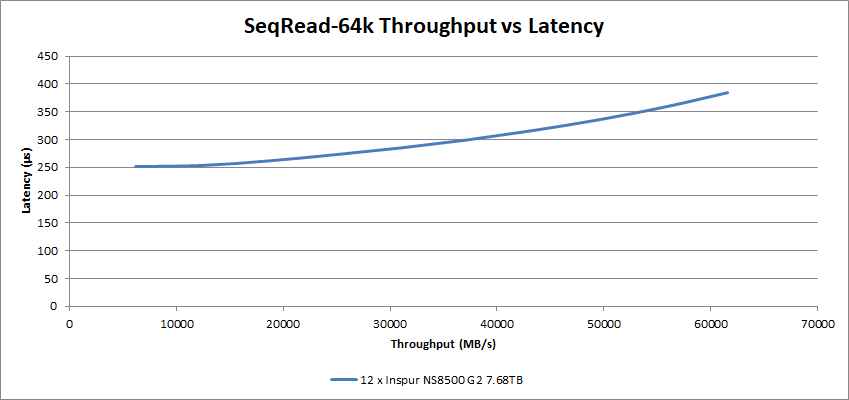
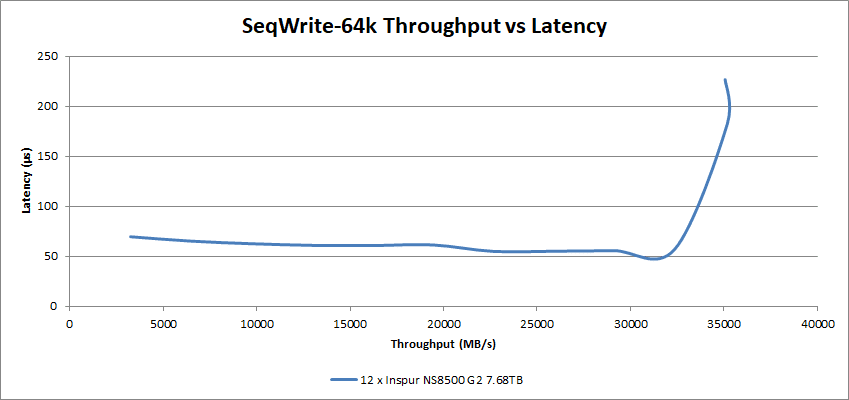
The Inspur NS8500 G2 SSDs hit 226µs latency at 35.1GB/s on the sequential write workload, however, note that at 32GB/s the latency was a very low 57µs.
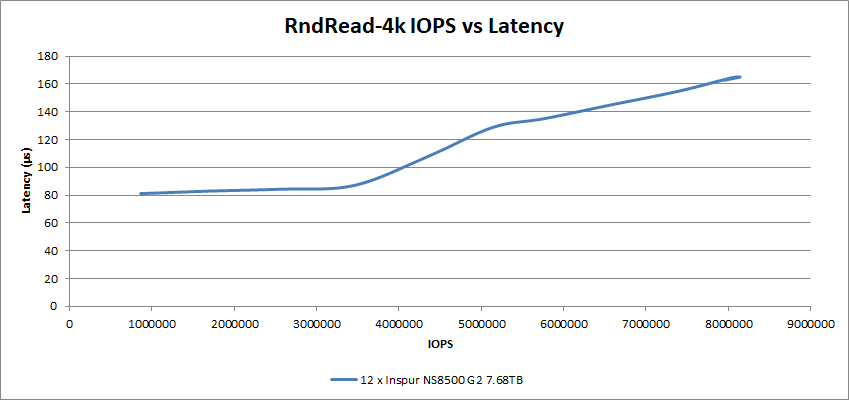
Random I/O Performance
Next, we performed the Random I/O tests at the 4k I/O size. The peak Random Read rate achieved by the 12 NS8500 G2 SSDs was over 8.14M IOPS at just under 165µs latency.
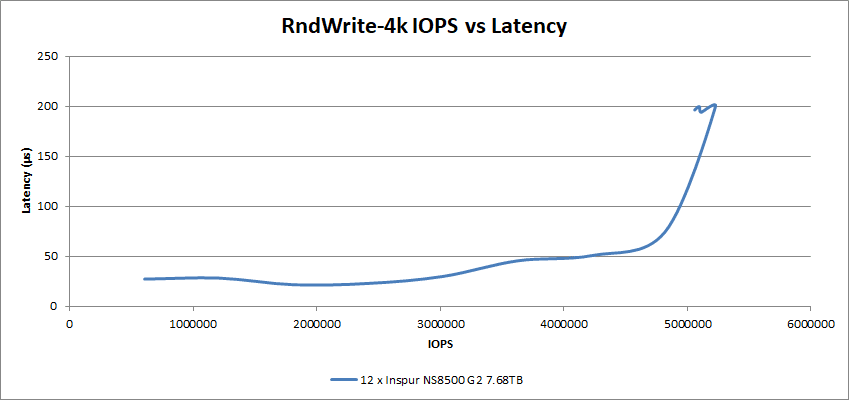
In the 4k Random Write testing, the 12 SSDs achieved just under 200µs at the write rate of over 5.22M IOPS. At around 4.8M IOPS the 12 drives still had a very low latency of just under 75µs.
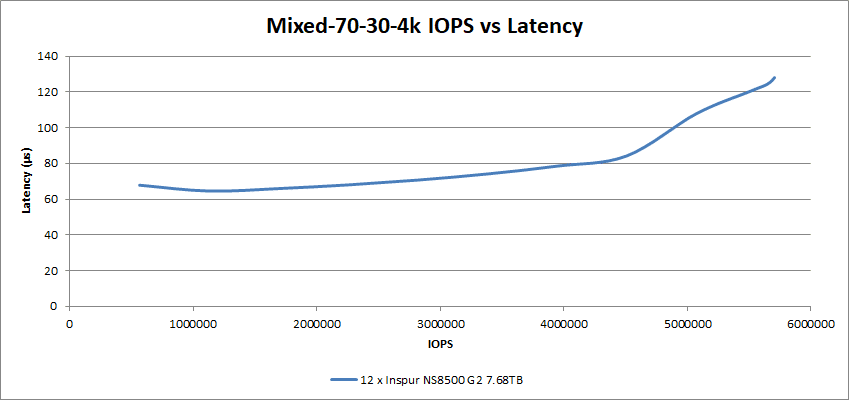
In the Mixed I/O workload tests, with a 70% read and 30% write workload, the 12 Inspur NS8500 G2 SSDs achieved a low 128µs latency at 5.7M IOPS.
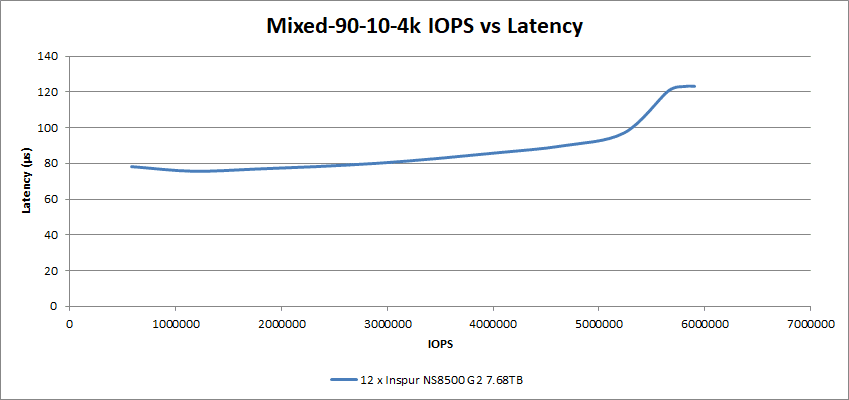
Ramping up the read percentage to 90% and lowering write to 10%, these 12 SSDs had a 123µs latency at 5.91M IOPS.
Synthetic Database Performance
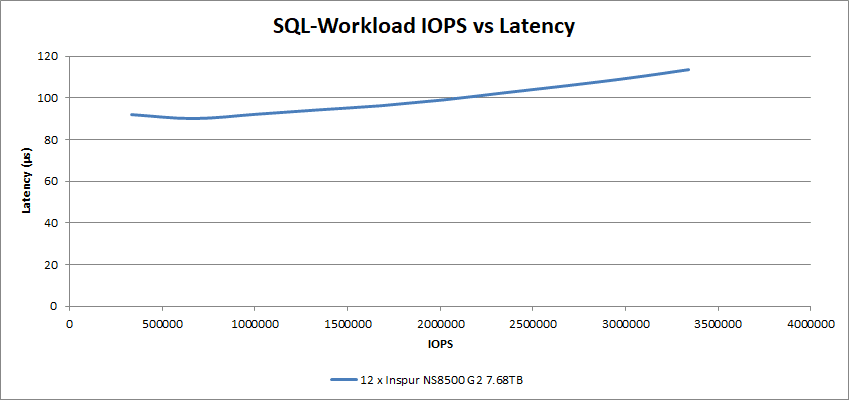
In our synthetic database testing, we achieved some high IOPS while maintaining low latency. The 12 Inspur NS8500 G2 drives achieved a latency of 113µs at 3.3M IOPS in the SQL Workload tests.
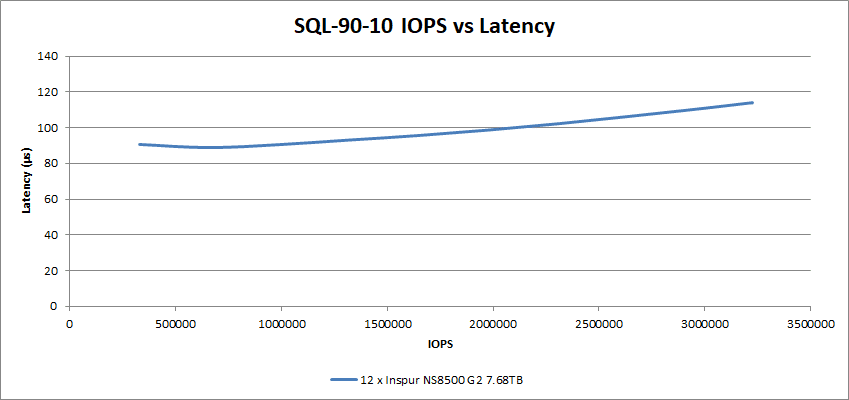
Adding write operations for the SQL 90-10 test, the 12 NS8500 G2 SSDs held on to the super-low latency, achieving 114µs at 3.22M IOPS.
This performance was maintained pretty well in the SQL 80-20 tests, achieving a latency of just under 116µs at 3.21M IOPS with an even greater write percentage.
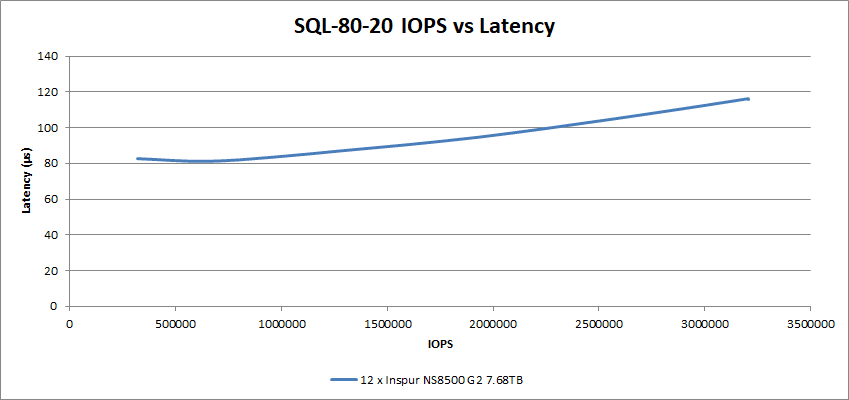
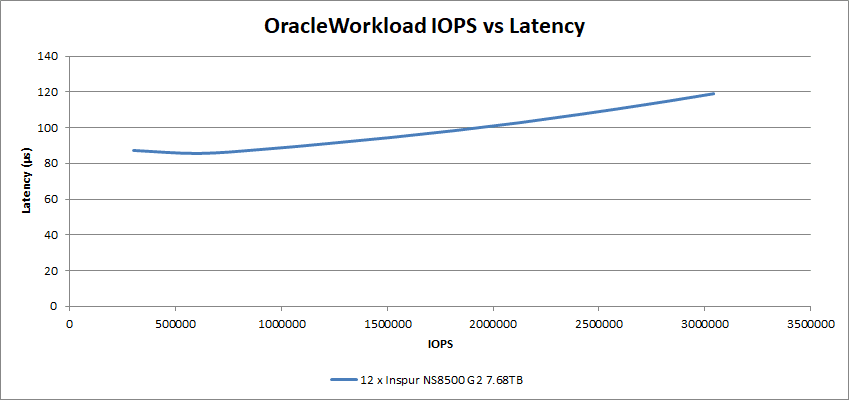
In the Oracle Workload testing, the 12 SSDs performed with a 119µs latency at just over 3.04M IOPS.
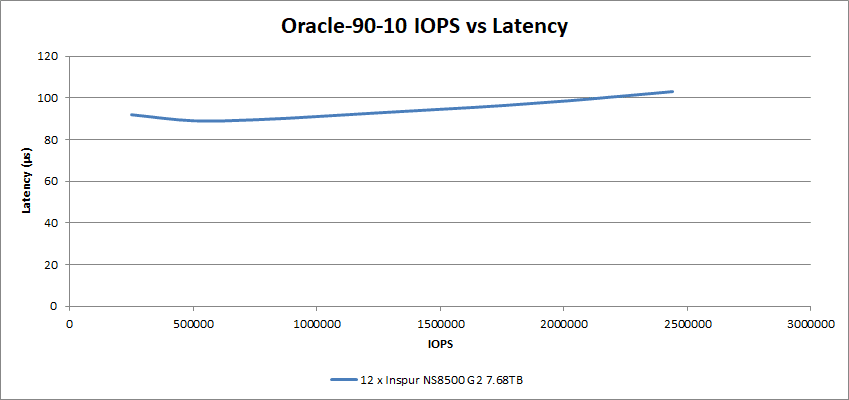
The addition of write operations in the Oracle 90-10 tests came in with a lower operation throughput, with 103µs at just under 2.44M IOPS.
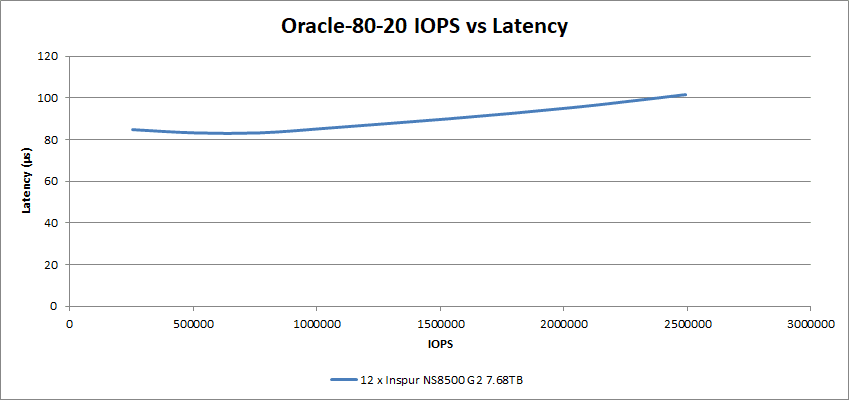
Adding more write operations in the Oracle 80-20 tests, the 12 SSDs performed at around 2.49M IOPS and achieved this at a latency of 101µs.
VDI Performance Tests
Our final series of tests are VDI Full Clone (FC) and Linked Clone (LC) testing suites.
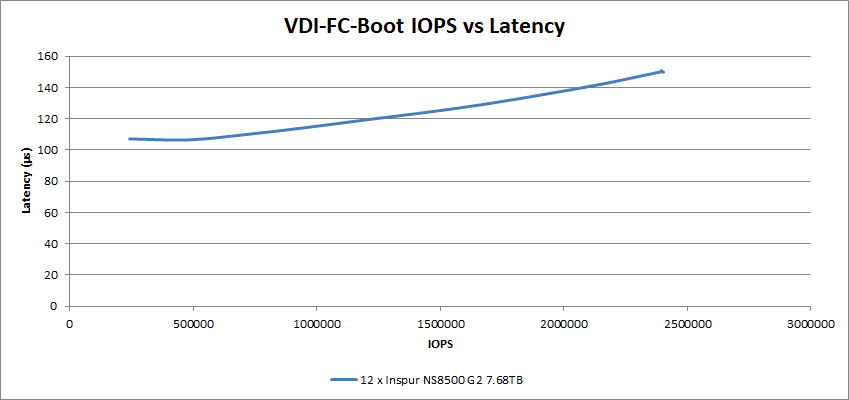
In the Full Clone tests, this graph shows the 150µs at 2.4M IOPS in our Boot test.
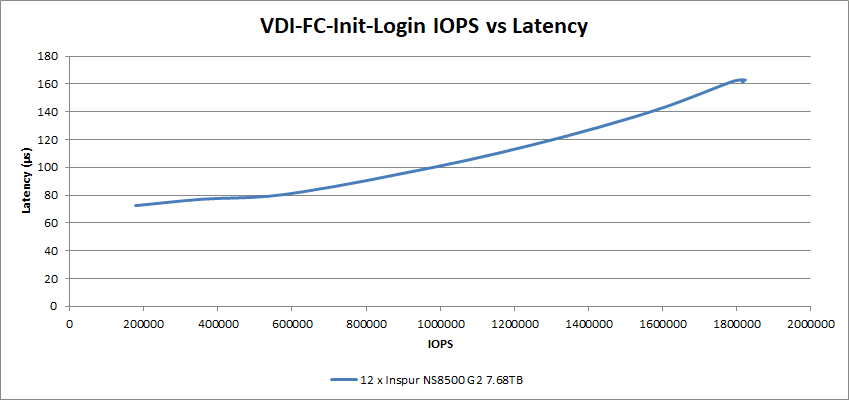
For the Full Clone Initial Login tests, the 12 NS8500 G2 SSDs achieved a latency of 163µs at 1.82M IOPS.
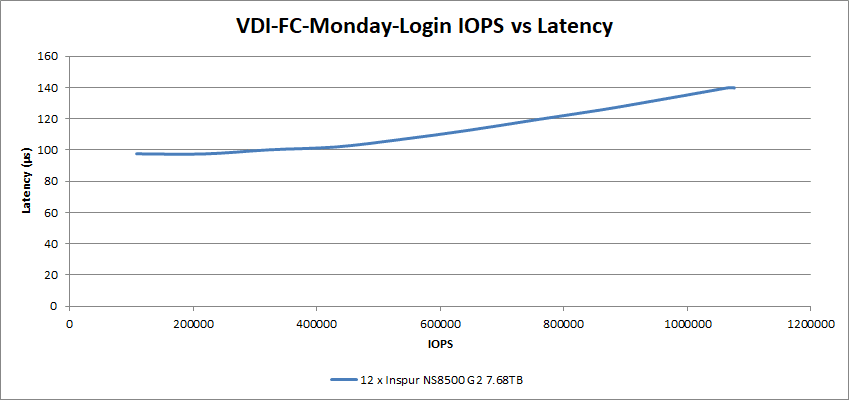
For the Full Clone Monday Login tests, the performance showed a latency of 140µs at 1.08M IOPS.
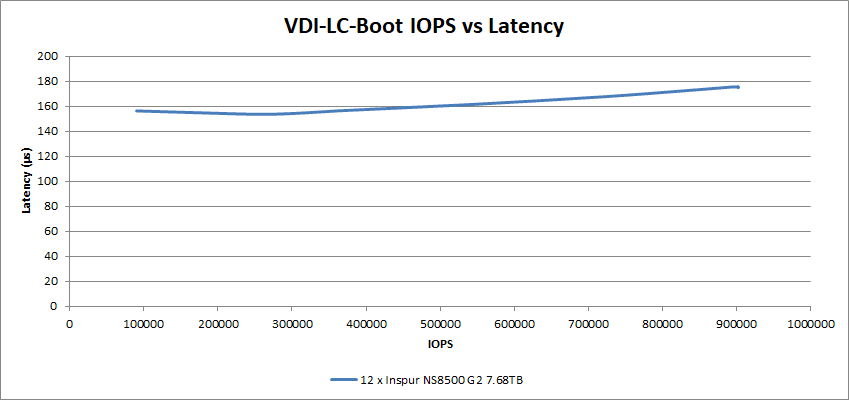
The Linked Clone tests are next up, and the 12 Inspur NS8500 G2 SSDs achieved 176µs at 903K IOPS for the Linked-Clone Boot test.
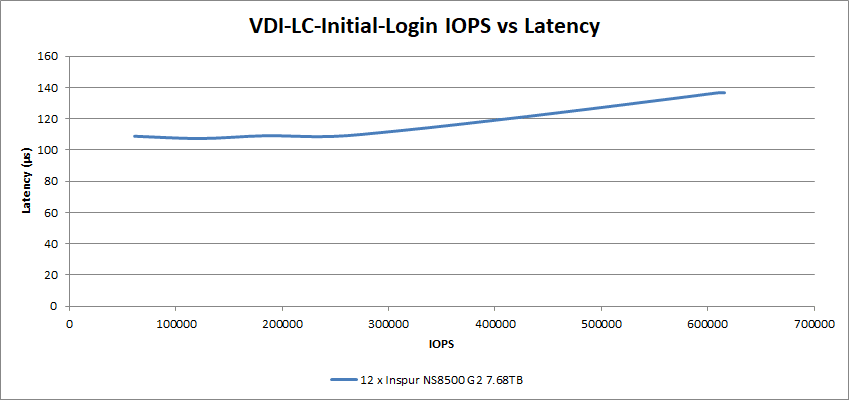
In the Linked Clone Initial Login test, the 12 SSDs peaked at a latency of 136µs at 615K IOPS.
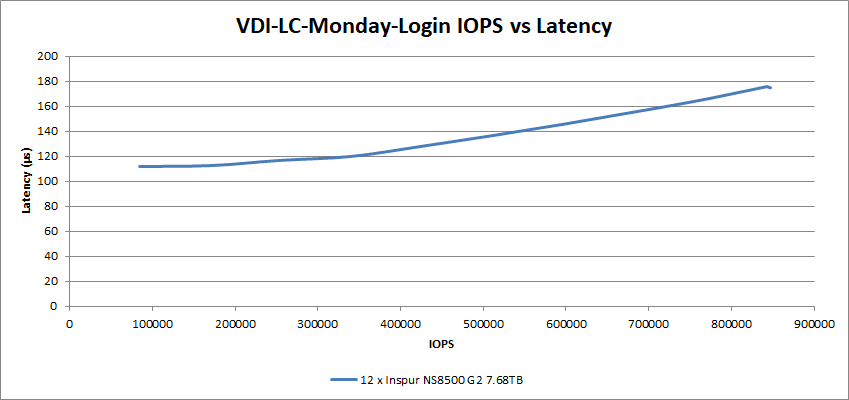
In our Linked Clone Monday Login testing, the 12 Inspur SSDs had a latency of 175µs at 847K IOPS.
Conclusion
The NS8500 G2 SSDs offer very strong performance, enabling a well-matched vertically integrated storage and compute offering from Inspur. Combining these with the Inspur NS5280M6 Server provides excellent performance for a wide range of applications, where the server itself is highly versatile in the number of configurations it can be purchased in. While we leveraged the model with 12 LFF bays, users can also opt for highly-dense SFF options.
When it comes to performance, the group of 12 Inspur NS8500 G2 SSDs offered a number of highlights in our synthetic VDBench workloads. Looking at large-block sequential performance, we measured in excess of 61.6GB/s read and 35.1GB/s write in our 64K tests. In small-block random, the SSDs offered over 8 million IOPS 4K random read and 4.8M IOPS write. In our SQL Server workload, the NS8500 G2 SSDs came in with 3.3M IOPS at 113µs of latency. We also saw strong VDI performance, highlighted by 2.4M IOPS in our VDI Boot workload.
According to Gartner, Inspur sits as the second-largest server vendor in the world. That’s impressive, their growth in servers is thanks in large part to their vast array of options, solving needs ranging from edge 5G to enterprise and OCP. We’ve recently seen this range in person, ranging from their highly dense E1.S solution at OCP to their also dense HDD M6 platform that squishes 26 hard drives into 2U in our lab. It’s not just the array of options though, Inspur has done well to actually ship products over the last few years with a strong supply chain.
Inspur is expanding its data center footprint by offering its own SSDs. This is an important step for the company, as they can now offer a more vertically integrated solution to customers. As we’ve seen in this report, the drives perform very well too, which should give them a differentiated story as there’s no other server vendor doing the same at scale. As the industry begins to adopt the latest EDSFF form factors, this should be an exciting time for Inspur to continue innovating throughout its portfolio.
Inspur has sponsored this report. All views and opinions expressed in this report are based on our unbiased view of the product(s) under consideration.




 Amazon
Amazon