AMD has announced the general availability of 3rd-gen AMD EPYC processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology (previously codenamed “Milan-X”), the world’s first data center CPU that leverages 3D die stacking. These new processors feature the Zen 3 core architecture and expand on the already impressive 3rd Gen EPYC portfolio. Compared to non-stacked 3rd-Gen EPYC processors, AMD indicates claims an increase of up to 66 percent in performance across a range of technical computing workloads.
The new AMD EPYC processors triple the L3 cache to 768MB or 1.5GB per 2P server–an industry high. It can deliver the same socket, software compatibility and modern security features as the non-3D V-Cache CPUs, while providing a new bar in performance for certain technical computing workloads.
Technical computing workloads will certainly benefit from increased cache size. AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology also solves the physical challenges behind this increase by bonding the AMD Zen 3 core to the cache module. As a result, this increases the amount of L3 while minimizing latency and increasing throughput.
Here are some examples from AMD on how their new processors will improve specific time-to-results workloads:
- EDA – The 16-core, AMD EPYC 7373X CPU can deliver up to 66 percent faster simulations on Synopsys VCS, when compared to the EPYC 73F3 CPU.
- FEA – The 64-core, AMD EPYC 7773X processor can deliver, on average, 44 percent more performance on Altair Radioss simulation applications compared to the competition’s top of stack processor.
- CFD – The 32-core AMD EPYC 7573X processor can solve an average of 88 percent more CFD problems per day than a comparable competitive 32-core count processor while running Ansys CFX.
Lower TCO and environmental sustainability
This improvement will allow their customers to deploy fewer servers, which in turn will help to reduce overall power consumption in the data center and lower total cost of ownership (TCO). Another nice benefit is the reduction in carbon footprint.
Rack space management is hugely important for HPC workloads, as organizations are always looking to find a perfect between performance, power and cooling, and licensing costs. For example, Dell’s 1-socket options (i.e., R6515 and R7515) will be very attractive to some organizations when paired with AMD’s new 32 and 64 core processors.
All of this combined makes the new 3rd Gen AMD EPYC processors with AMD 3D V-Cache a positive impact on environmental sustainability.
AMD EPYC processors w/ 3D V-Cache Specifications and Pricing
| Cores | Model | #CCD | TDP (W) | cTDP range (W) | Base Freq (GHz) | Max Boost Freq (up to GHz) | L3 Cache (MB) | DDR Channels | Price (1KU) |
| 64 | 7773X | 8 | 280 | 225-280 | 2.20 | 3.50 | 768 | 8 | $8,800 |
| 64 | 7763 (prior) | 8 | 280 | 225-280 | 2.45 | 3.50 | 256 | 8 | $8,640 |
| 32 | 7573X | 8 | 280 | 225-280 | 2.80 | 3.60 | 768 | 8 | $5,590 |
| 24 | 7473X | 8 | 240 | 225-280 | 2.80 | 3.70 | 768 | 8 | $3,900 |
| 16 | 7373X | 8 | 240 | 225-280 | 3.05 | 3.80 | 768 | 8 | $4,185 |
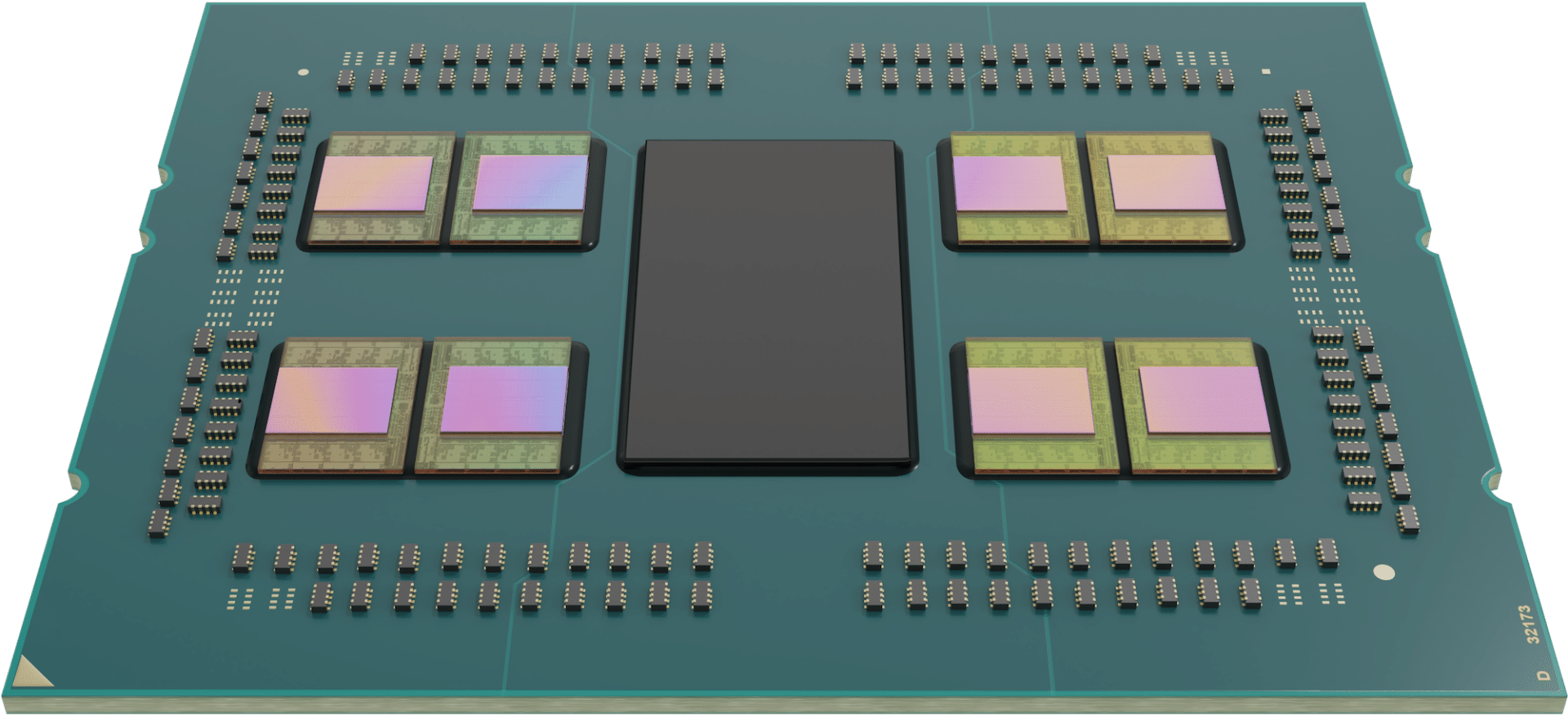
All Milan-X models have 8 Core Complex Dies (CCDs), each of which has 96MB in L3 cache for a total of 786MB (any single core can access the full 96MB as well).
Are AMD EPYC Processors with AMD 3D V-Cache Right for You?
AMD has been quite transparent about how their new CPUs won’t benefit every organization, as they have been designed for specific use cases.
As such, AMD indicates the following workloads that might be a good fit for Milan-X:
- Workloads that are sensitive to L3 cache size
- Workloads that have high L3 cache capacity misses (for example, the data set is often too large for L3 cache)
- Workloads that have high L3 cache conflict misses (for example, the data pulled into cache has low associativity)
Some areas that might have these kinds of workloads include fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), electronic design automation (EDA) and structural analysis.
That said, workloads that already have L3 cache miss rates near the zero mark, have high L3 cache coherency misses (i.e., data is highly shared between cores), or might be CPU-sensitive (but only use data rather than operating on it iteratively) likely won’t find much benefit here.
Partners Announce Support for AMD EPYC Processors with AMD 3D V-Cache
AMD has dozens of partners, including Dell Technologies, who announced support for the new 3rd Gen AMD EPYC 7003 processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology. This will allow their PowerEdge servers to address the increasing number of nodes (as well as the complexity of communication between them) in HPC workloads. Tripling the L3 cache to 768MB and optimizing data latency will improve overall PowerEdge HPC performance, particularly in technical computing environments as we indicated above.
Dell indicates that technical workloads running the 7003 processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology will increase performance by up to 61% Ansys CFX (Turbomachinery CFD software) and up to 56% max for FEA on Altair Radioss (structural analysis solver) compared to the 3rd-gen AMD processors without 3D V-Cache.
For example, a PowerEdge R7525 equipped with an EPYC 7773X CPU set a world record by running 86,000 users on the SAP SD (sales and distribution) benchmark, which is an increase of 14 percent over the previous record. The SD benchmark is an indicator of how well organizations can store and manage customer and product-related data. Being able to access this type of data at high speeds and low latency is paramount in business architecture.
The increase to 768MB in L3 cache also allows the PowerEdge servers to support digital manufacturing workloads due to the significant improvements in memory latency and bandwidth. Applications like computational fluid dynamics and finite element analysis will benefit the most here. Dell also reports a reduction in memory latency of roughly 25-35%, which will benefit Register Transfer Level (RTL) simulations as well as important implications for HPC in the financial industry, Dell claims.
Supermicro has also announced support for the 3rd-Gen AMD EPYC Processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology in their advanced servers. The HPC company has indicated their high density, performance-optimized SuperBlade, multi-node optimized TwinPro and the dual-processor optimized Ultra systems will show significant performance gains when using the new Milan-X processors in technical computing environments.
For example, the SuperBlade server has achieved up to a 17% improvement using compared to the models without AMD 3D V-Cache technology, claiming world records for the SPECjbb 2015-Distributed critical-jOPS and max-jOPS benchmark.
Moreover, using the new AMD processor allows the Supermicro SuperBlade to contain up to 20 CPUs in an 8U chassis, including a network switch built into the chassis. Shared cooling and power systems reduce the power usage, while maximum memory can reach up to 40TB in a fully populated 8U chassis.




 Amazon
Amazon