Broadcom introduced Thor Ultra, the industry’s first 800G AI Ethernet NIC that is fully compliant with the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) specifications. It was designed for clusters with more than 100,000 XPUs. Thor Ultra targets the bottlenecks that constrain traditional RDMA, adding packet-level multipathing, out-of-order data placement, hardware SACK-based retransmission, and a fully programmable congestion-control pipeline.
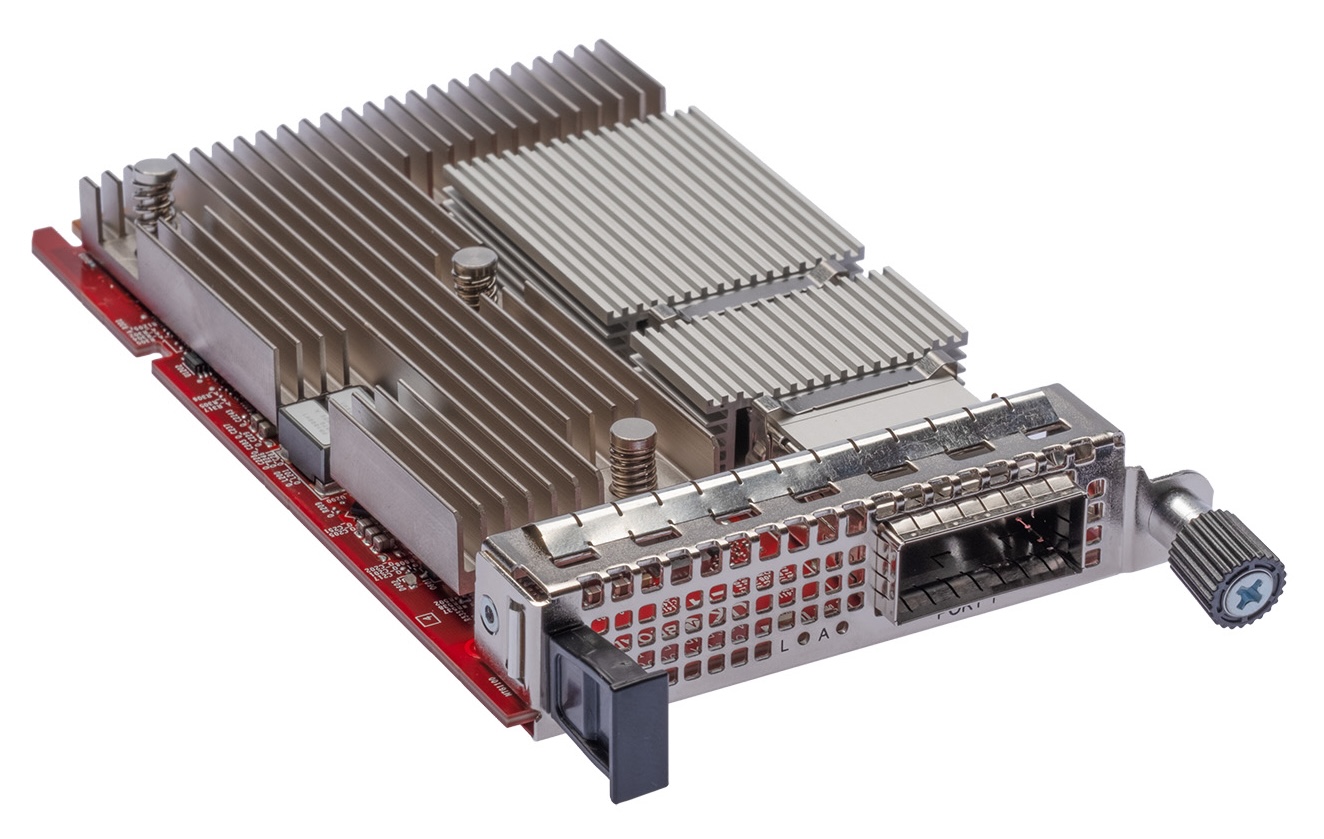
Thor Ultra OCP card
The NIC seamlessly integrates with Broadcom Tomahawk 6 and is compatible with any UEC-compliant switch lineup. Broadcom highlights its security features, including line-rate PSP encryption, secure boot, and attestation. The NIC also offers deployment versatility with 100G/200G SerDes and supports various usage models, including chiplet, IP, PCIe, and OCP 3.0 cards. Thor Ultra serves as a forward-thinking, high-bandwidth, telemetry-enabled component suitable for Ethernet-based AI infrastructures.
RDMA for AI Has Hit Its Limits
AI data centers are transitioning from predictable HPC-style processes to unpredictable, bursty, and distributed AI tasks, including training, fine-tuning, and large-scale inference. Under these conditions, traditional RDMA (as used in many RoCE implementations) experiences significant strain. Contributing to the RDMA constraints include:
- The absence of genuine multipathing at the packet level forces data flows to use only one path, increasing tail latency during incast events and microbursts.
- In-order placement requirements hinder optimal PCIe utilization when packets arrive out of sequence, causing stalls and head-of-line blocking at the host.
- Go-Back-N retransmissions increase congestion and lead to bandwidth waste, and recovery from losses is slow.
- Tuning congestion control across leaf-spine fabrics at the 100K-node scale is challenging and often varies by vendor.
Thor Ultra overcomes these limitations by aligning RDMA semantics more closely with the requirements of large-scale AI fabrics, supporting fine-grained load distribution, reordering tolerance, rapid loss recovery, and programmable congestion control that adapts as UEC evolves.
Architecture and Features
Thor Ultra is designed to anchor UEC-compliant AI Ethernet fabrics, featuring a NIC that eliminates bottlenecks on both the host and fabric sides. Thor Ultra features include:
- Thor Ultra’s RDMA pipeline uses packet-level multipathing to distribute traffic across multiple paths and supports out-of-order packets directly in XPU memory. It ensures reliability through SACK and retransmissions and features a fully programmable congestion control that supports various algorithms for policy unification and flexibility.
- Thor Ultra prioritized full UEC compliance, supporting behaviors for reliability, congestion signaling, and telemetry. It is compatible with Broadcom Tomahawk 6 and other UEC switches, promoting an open Ethernet approach to avoid lock-in and enable mixed-vendor fabrics.
- Thor Ultra’s line-rate security includes hardware-accelerated encryption/decryption, secure boot with signed firmware, and device attestation, ensuring supply-chain and runtime integrity in multi-tenant AI clusters.
- Scale-out UEC-compliant telemetry features, such as packet trimming and explicit congestion signaling, are supported, enhancing observability, closed-loop congestion control tuning, and quick fault isolation in scale-out fabrics.
- The NIC supports 100G and 200G SerDes configurations for flexible port and upgrade options. It uses thermally efficient passive copper DACs up to five meters for short-range rack connections, reducing power and cost. The models include chiplet/IP for custom boards and standard PCIe and OCP 3.0 form factors, all of which share firmware and tools for easier management.
Ethernet AI Fabrics vs. Proprietary Alternatives
The launch of Thor Ultra aligns with key competitive aspects. Proprietary AI interconnects include InfiniBand and vendor-specific Ethernet overlays. NVIDIA’s InfiniBand solutions, such as ConnectX/BlueField and Quantum switches, offer features like SHARP, adaptive routing, and optimized congestion control. However, these come with vendor lock-in and increased total cost of ownership (TCO). Thor Ultra’s UEC compliance and advanced RDMA capabilities are designed to match or surpass tail-latency and throughput performance using standard Ethernet. This offers buyers a standards-based alternative, ensuring supply flexibility and familiar toolchains.
Unlike NVIDIA’s Ethernet strategy with Spectrum-X, which targets AI fabrics with proprietary scheduling/CC, Broadcom is “UEC-first” openness, plus Tomahawk/Jericho switch scale and a merchant optics ecosystem breadth. However, for many CSPs, like AWS and Google, that deploy custom hardware, UEC may not be a strong selling point. Although deploying custom hardware may cause some heartburn, they believe being in control is more critical than UEC compliance.
Intel, AMD (Pensando), Marvell, and NVIDIA provide competing Ethernet NIC, SmartNIC, and DPU solutions for AI clusters, with RoCEv2 improvements and host offloads. Thor Ultra distinguishes itself by delivering 800G line rate, packet-level multipathing with out-of-order placement, hardware SACK retransmissions, and a programmable congestion control engine compatible with UEC.
Broadcom’s Tomahawk 6 and Jericho are leading in hyperscale merchant Ethernet. Thor Ultra offers a comprehensive Ethernet AI infrastructure. For operators hesitant about single-vendor ecosystems, UEC compliance and interoperability with other top vendors allow flexibility, enabling Broadcom NICs to work with various UEC switches or vice versa.
Thor Ultra boosts Ethernet’s viability for AI at over 100,000 nodes by addressing key RoCE challenges and promoting a standards-based approach, rather than relying on a single vendor’s fabric.
AI Data Center Design
Thor Ultra’s capabilities nudge architects toward a few design shifts, which include:
- Fabric standardization on UEC: Anticipate reference designs that define UEC-compliant NICs and switches, unifying congestion signaling, telemetry, and reliability standards among vendors. This minimizes integration challenges and simplifies multi-source procurement.
- Ethernet-first AI pods feature predictable tail latency through packet-level multipathing and support for out-of-order placement. These pod designs utilize 800G NICs connected via 100G/200G SerDes lanes to ToR/leaf switches, layered over deep ECMP fabrics. This setup allows designers to be more aggressive with path diversity and oversubscription, all while maintaining low p99 and p99.9 latencies.
- Programmable congestion control as an operational knob: With CC running in NIC silicon but programmable, operators can adapt to workload phases (data-parallel training vs. pipeline-parallel inference) and fabric conditions without hardware swaps. Expect A/B testing of receiver- vs. sender-based schemes and closed-loop control using UEC telemetry.
- Simpler host datapaths and PCIe efficiency: Out-of-order placement into XPU memory and hardware SACK reduce CPU/XPU involvement in reorder and recovery, freeing host cycles and smoothing PCIe bandwidth utilization. This matters for GPU/accelerator servers already running at the edge of PCIe and memory bandwidth envelopes.
- Security baked into the NIC: Line-rate encryption, secure boot, and hardware-attestation ease compliance in multi-tenant clusters, especially when sharing fabric between training and inference tenants or when partitioning across internal teams.
- Cabling and power TCO: Passive copper DACs up to 5m for NIC-to-ToR runs can lower optics power budgets and simplify rack-level thermals.
- Operational telemetry and SLOs: UEC telemetry primitives, such as packet trimming and explicit congestion signals, enable tighter SLO management and faster RCA at scale. Integrations into existing NetOps/AI Ops pipelines will be a selection criterion.
Deployment
Thor Ultra supports 100G/200G SerDes configurations, ships as a chiplet/IP for custom integrations, and as standard PCIe and OCP 3.0 cards. All variants share a unified firmware, driver, and software toolchain to streamline fleet operations. Broadcom positions Thor Ultra to “drop in” alongside Tomahawk 6, with stated compatibility for UEC-compliant switches from other vendors.
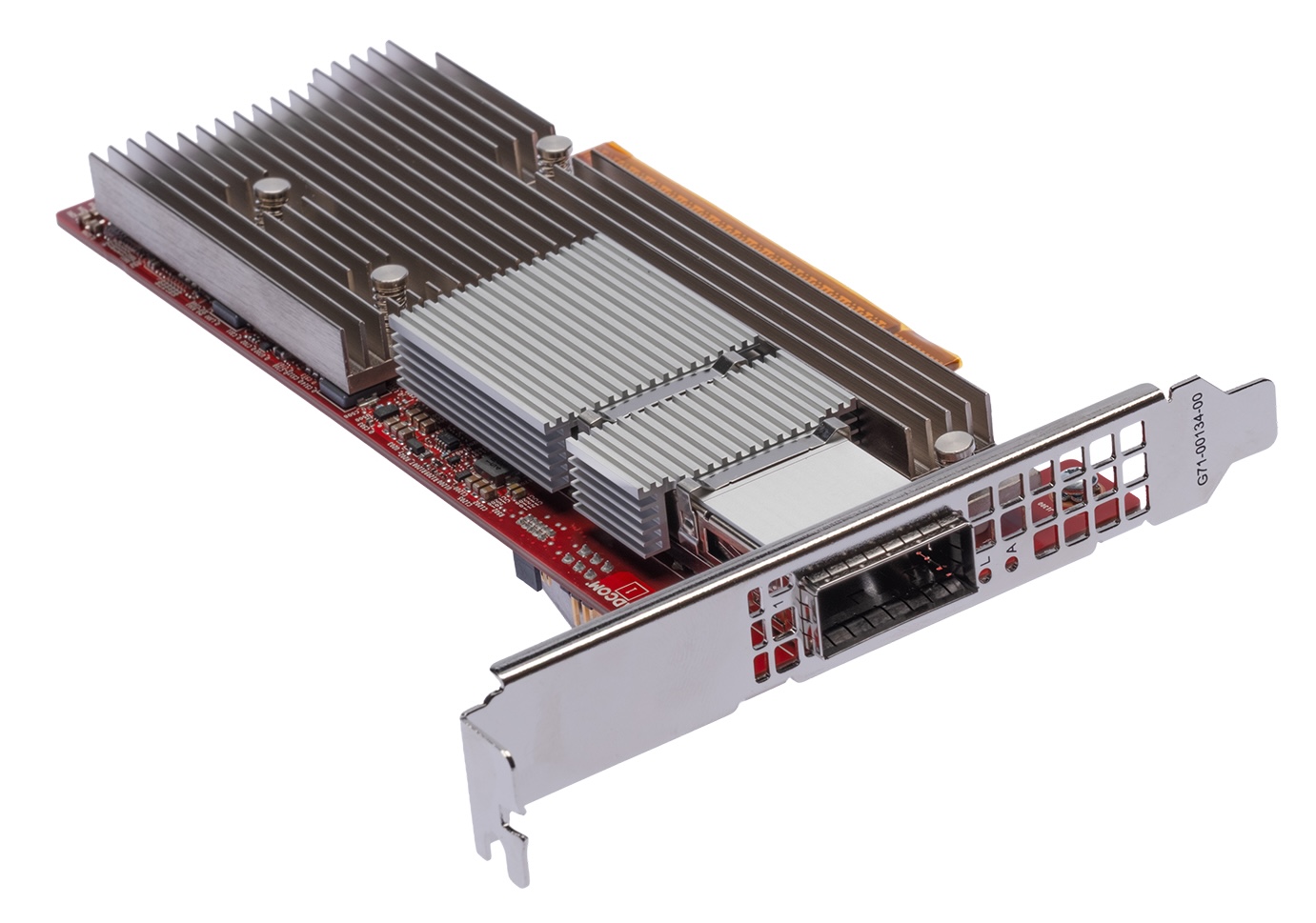
Thor Ultra PCIe card
Broadcom introduces Thor Ultra as a significant breakthrough in AI Ethernet. This 800G NIC fully supports UEC and offers advanced RDMA capabilities, focusing on performance, scalability, and openness. It enhances the Ethernet-for-AI story by providing an 800G NIC that addresses key limitations of traditional RoCE at hyperscale, including a lack of packet-level multipathing, unreliable in-order delivery, slow retransmissions, and fragile congestion control.
Availability
Broadcom is sampling the Thor Ultra with select customers.




 Amazon
Amazon