NVIDIA has announced the specifications for its Vera Rubin NVL144 MGX-generation open-architecture rack servers. Over 50 MGX partners are preparing for this release, along with ecosystem support for NVIDIA Kyber, which links 576 Rubin Ultra GPUs and is built to meet increasing inference demands.
In September, NVIDIA announced an expanded partnership with Intel. Meanwhile, Intel announced its new Xeon 6 processors, with one of the processors serving as the host CPU for the NVIDIA DGX B300, the company’s latest generation of AI-accelerated systems. The NVIDIA DGX B300 integrates the Intel Xeon 6776P, which plays a vital role in managing, orchestrating, and supporting the AI-accelerated system. With robust memory capacity and bandwidth, the Xeon 6776P supports the growing needs of AI models and datasets.

The Xeon 6776P is designed as a “GPU host” CPU with Priority Core Turbo (PCT) and Intel Speed Select-Turbo Frequency (SST‑TF) so a small set of cores can boost higher and handle latency‑sensitive orchestration while other cores run at base clocks. This helps improve effective GPU utilization in NVLink clusters by reducing stalls in preprocessing, KV‑cache handling, and scheduling.
Vera Rubin NVL144: Designed to Scale for AI Factories
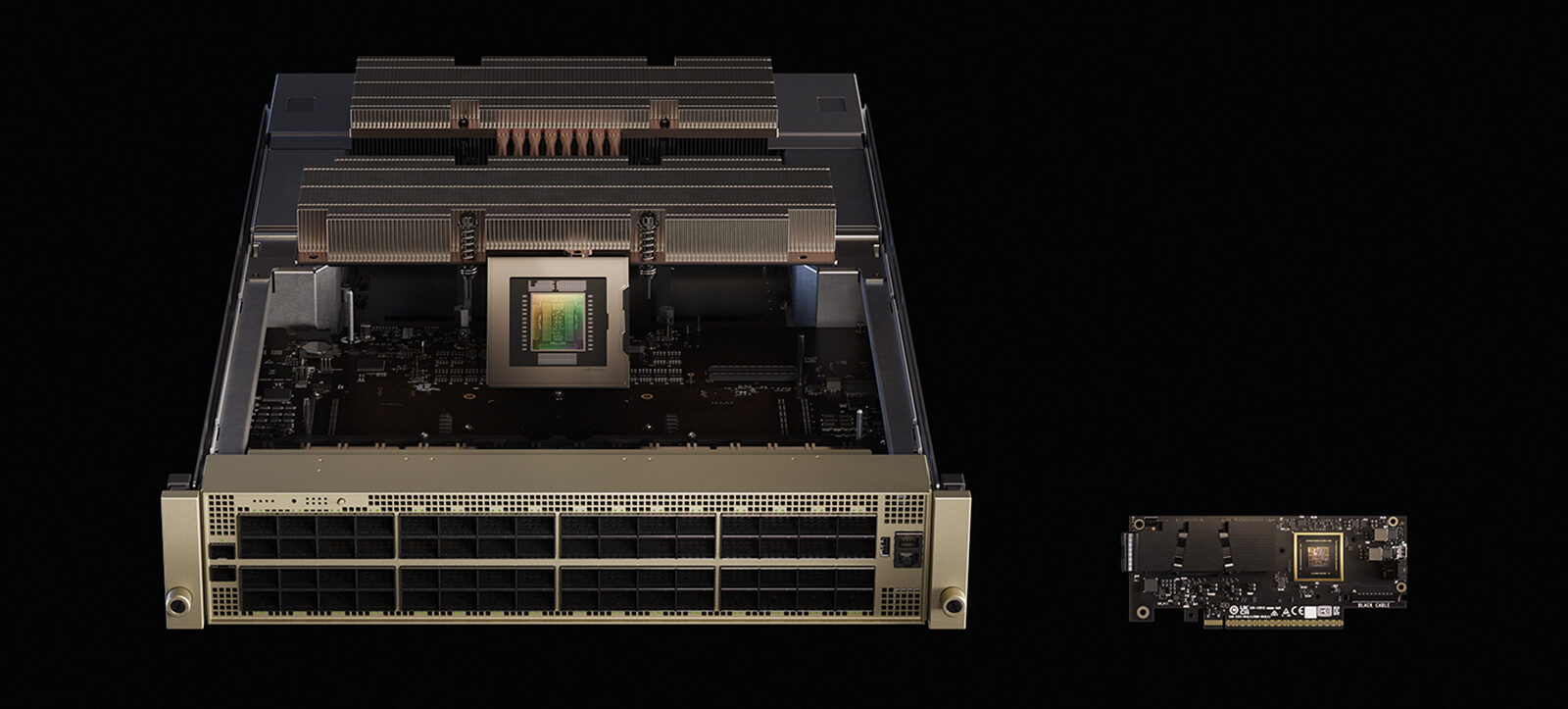
The Vera Rubin NVL144 MGX compute tray features an energy-efficient, fully liquid-cooled, modular design. Its central printed circuit board midplane replaces conventional cable connections, enabling quicker assembly and easier maintenance. It also includes modular expansion bays for NVIDIA ConnectX-9 800GB/s networking and NVIDIA Rubin CPX, supporting large-scale inference tasks.
The NVIDIA Vera Rubin NVL144 represents a significant advancement in accelerated computing architecture and AI capabilities. It is designed to support advanced reasoning engines and meet the needs of AI agents.
The core design is based on the MGX rack architecture and will be supported by over 50 MGX system and component partners. NVIDIA intends to contribute the enhanced rack and compute tray innovations as an open standard to the OCP consortium.
Its standards for compute trays and racks enable partners to assemble modular systems and scale more quickly with the architecture. The Vera Rubin NVL144 rack design features energy-efficient 45°C liquid cooling, a new liquid-cooled busbar for enhanced performance, and 20 times more energy storage to maintain consistent power.
The MGX enhancements to compute tray and rack architecture improve AI factory performance and make assembly easier, allowing for a quick scaling up to gigawatt-level AI infrastructure.
NVIDIA NVLink Fusion Ecosystem Expands
In addition to hardware, NVIDIA NVLink Fusion is gaining momentum, enabling companies to seamlessly integrate their semi-custom silicon into a highly optimized, widely deployed data center architecture, reducing complexity and accelerating time to market.
Intel and Samsung Foundry are joining the NVLink Fusion ecosystem, which encompasses custom silicon designers, CPU and IP partners, enabling AI factories to rapidly scale and manage intensive workloads for model training and agentic AI inference.
- As part of the recently announced NVIDIA and Intel collaboration, Intel will build x86 CPUs that integrate into NVIDIA infrastructure platforms using NVLink Fusion.
- Samsung Foundry has partnered with NVIDIA to meet growing demand for custom CPUs and custom XPUs, offering design-to-manufacturing experience for custom silicon.
NVIDIA Kyber Rack
Over 20 industry partners are presenting new silicon, components, power systems, and support for next-generation 800-volt direct current (VDC) data centers. These centers, designed for the gigawatt era, will support NVIDIA’s Kyber rack architecture.

Foxconn has shared details about its 40-megawatt Taiwan data center, Kaohsiung-1, which is being built for the 800 VDC era. Other industry leaders, including CoreWeave, Lambda, Nebius, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and Together AI, are also planning data centers with 800-volt infrastructure in mind. Additionally, Vertiv has introduced its 800 VDC MGX reference architecture, a solution designed to optimize space, cost, and energy efficiency while offering a complete power and cooling infrastructure. Meanwhile, HPE is supporting products for NVIDIA Kyber and NVIDIA Spectrum-XGS Ethernet scale-out technology, both integral parts of the Spectrum-X Ethernet platform.
Switching to 800 VDC infrastructure from conventional 415 or 480 VAC three-phase systems offers greater scalability, improved energy efficiency, reduced material consumption, and enhanced performance in data centers. The electric vehicle and solar sectors have already implemented 800 VDC infrastructure to achieve these benefits.
NVIDIA Kyber Rack Server Generation
The OCP ecosystem is also preparing for NVIDIA Kyber, which features innovations in 800 VDC power delivery, liquid cooling, and mechanical design.
These innovations will facilitate the transition to the rack server generation NVIDIA Kyber, the successor to NVIDIA Oberon, which is expected to feature a high-density platform with 576 NVIDIA Rubin Ultra GPUs by 2027.
The best approach to address high-power distribution challenges is to raise the voltage. Moving from a standard 415 or 480 VAC three-phase system to an 800 VDC system offers several advantages.
The ongoing transition enables rack server partners to upgrade their in-rack components from 54 VDC to 800 VDC, enhancing performance. At the event, a collaborative ecosystem of direct current infrastructure providers, power system and cooling partners, and silicon manufacturers worked together on open standards for the MGX rack server reference architecture.
NVIDIA Kyber aims to boost rack GPU density, enhance network capacity, and optimize the performance of large-scale AI systems. It features vertical mounting of compute blades, supporting up to 18 blades per chassis. Furthermore, NVIDIA’s specialized NVLink switch blades are positioned at the back via a cable-free midplane, facilitating seamless, scalable network connectivity.
Over 150% more power is transmitted through the same copper with 800 VDC, eliminating the need for 200-kg copper busbars to feed a single rack.
Kyber is set to become a core component of hyperscale AI data centers, boosting performance, efficiency, and reliability for advanced generative AI tasks. NVIDIA Kyber racks enable customers to significantly reduce copper usage, resulting in millions of dollars in cost savings.
Scaling the Next Generation of AI Factories
More than 20 NVIDIA partners are helping deliver rack servers with open standards, enabling the future gigawatt AI factories.
- Silicon providers: Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), AOS, EPC, Infineon, Innoscience, MPS, Navitas, onsemi, Power Integrations, Renesas, Richtek, ROHM, STMicroelectronics, and Texas Instruments
- Power system component providers: Bizlink, Delta, Flex, GE Vernova, Lead Wealth, LITEON, and Megmeet
- Data center power system providers: ABB, Eaton, GE Vernova, Heron Power, Hitachi Energy, Mitsubishi Electric, Schneider Electric, Siemens, and Vertiv
NVIDIA is a leading contributor to OCP standards across multiple hardware generations, including key portions of the NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 system electro-mechanical design. The same MGX rack footprint supports GB300 NVL72 and will support Vera Rubin NVL144, Vera Rubin NVL144 CPX, and Vera Rubin CPX for higher performance and fast deployments.




 Amazon
Amazon